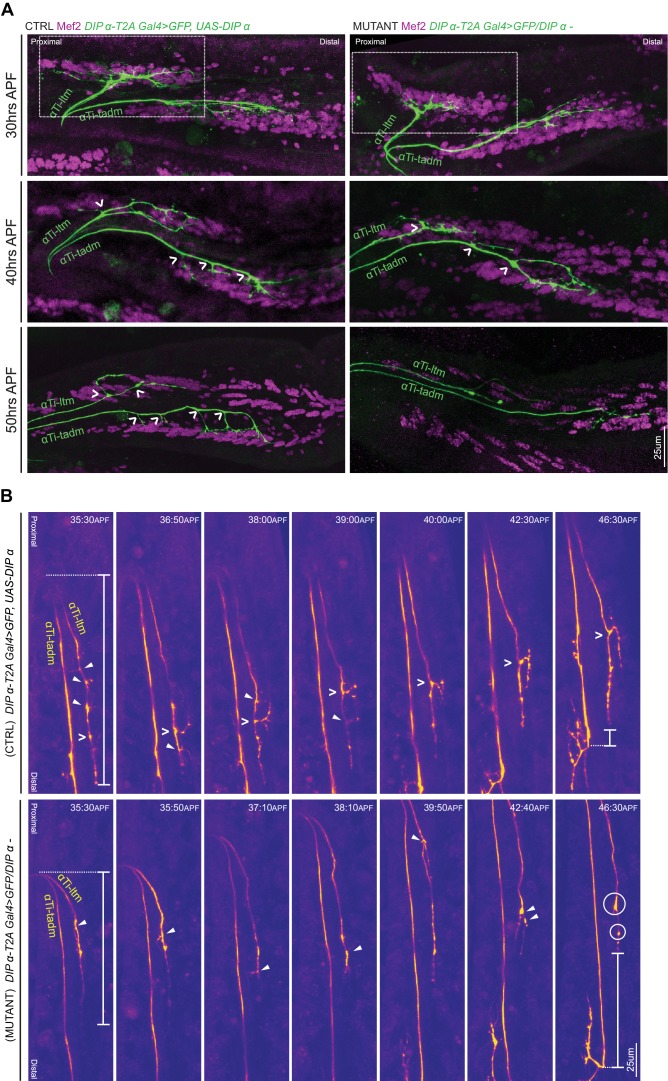
Figure 6. DIP-α is required for terminal axon lengthening and branching 30 to 45 hr APF.
(A) Terminal axon branching of control (left) and DIP-α mutant (right) αTi-ltm and αTi-tadm leg MNs at 30 hr (top), 40 hr (middle) and 50 hr (bottom) APF using DIP-α-T2A-Gal4 > UAS-DIP-α and DIP-α-T2A-Gal4/DIP-α–, respectively. Axons are labeled using DIP-α-T2A-Gal4 > 20XUAS-6XGFP (green) and muscles are labeled with antibody against Mef2 (magenta). White arrowheads demarcate branch points along the axon terminal. At 50 hr APF, mutant αTi-ltm axons lack a prominent contralateral branch and mutant αTi-tadm axons lack four contralateral branches and retain the distal-most branch. White-dotted box denotes magnified inset in Figure 5—figure supplement 1A (scale bar: 25 μm). (B) Snapshots from time-lapse videos (Video 4, Video 5) comparing control (top) and mutant (bottom) αTi-ltm and αTi-tadm axons between ~35 hr and 45 hr APF (time-stamp is located on the top-right corner of each snapshot). Axons are labeled using DIP-α-T2A-Gal4 > 20XUAS-6XGFP (yellow). White open arrowheads demarcate the contralateral branch point on the αTi-ltm axon in the control sample while filled white arrowheads demarcate assorted dynamic filopodial projections along the αTi-ltm axon in both control and mutant samples. The distal-most tip of the αTi-ltm axon is more proximally located in the mutant sample compared to the control at ~35 hr APF (far left), as measured from the axon ‘bend’ at the joint between the distal Femur and proximal Tibia (denoted by white vertical bars) as well as at ~45 hr APF (far right), as measured from the distal most branch of αTi-tadm (denoted by white vertical bars). White circles demarcate globular punctate structures that form on the mutant αTi-ltm axon by ~45 hr APF (far right). (scale bar: 25 μm).