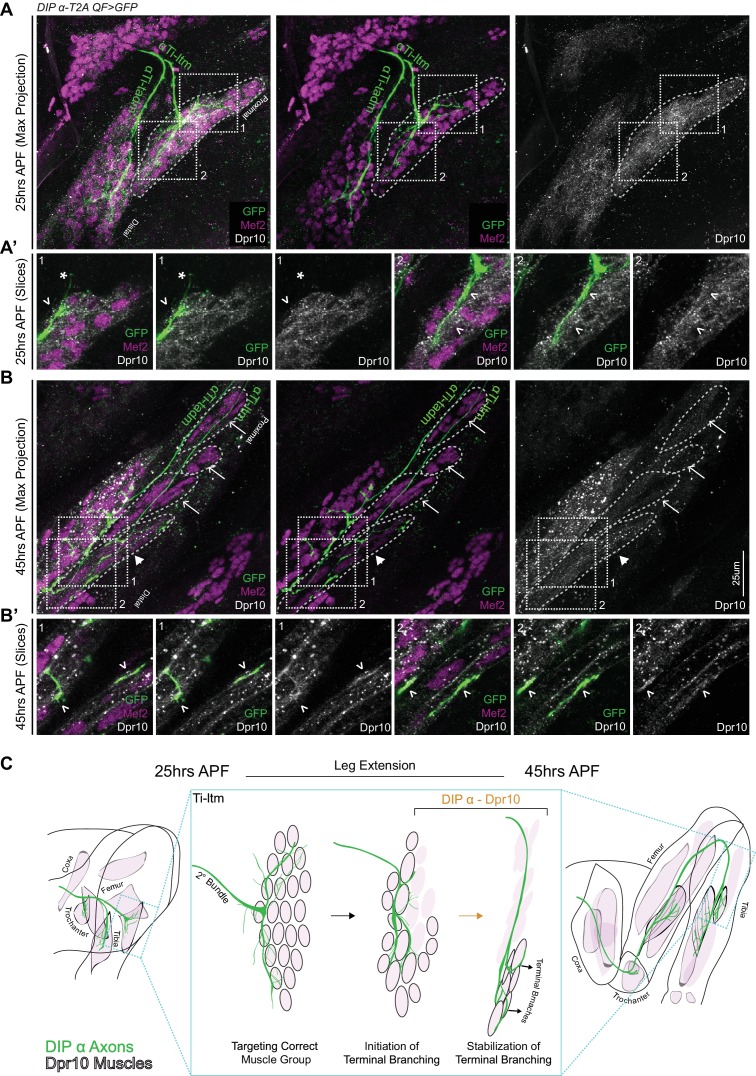
Figure 7. Dpr10 Expression is gradually restricted to distal fibers of the Ti-ltm 30 to 45 hr APF.
(A–B) Dpr10 protein expression (grey) in the developing Ti-ltm and proximal tadm, labeled by Mef2 (magenta) along with αTi-ltm and αTi-tadm axons labeled by DIP-α-T2AQF > 10XQUAS-6XGFP (green) at 25 hr (A) and 45 hr (B) APF. Left: GFP, Mef2 and Dpr10; middle: GFP and Mef2; right: Dpr10. (A’,B’) show magnified single slice images of the dashed boxes indicated in A,B. While Dpr10 is widely expressed in the entire Ti-ltm at 25 hr APF (A) (dashed boundary demarcates immature Ti-ltm), it is later restricted to the distal muscle fibers of the Ti-ltm at 45 hr APF (B) (white arrowhead, dashed boundaries demarcate distinct groups of muscle fibers of the Ti-ltm). Lack of Dpr10 expression in the proximal muscles fibers of the Ti-ltm at 45 hr APF (B) are denoted by white arrows. Dpr10 is continuously expressed in the tadm. (scale bar: 25 μm). At 25 hr APF (A’) there is no correlation between Dpr10 protein and αTi-ltm innervation, denoted by white arrowheads. By 45 hr APF (B’) higher levels of Dpr10 protein are seen in regions innervated by the αTi-ltm terminal branches (white arrowheads). (C) Schematic representation of a DIP-α expressing axon (green) innervating Dpr10 expressing muscle precursors (black outlined pink cells) during the course of development between 25 to 45 hr APF, depicting the restriction of Dpr10 to specific muscle fibers targeted by the DIP-α expressing axon. Leg extension occurs between ~30 to 40 hr APF.