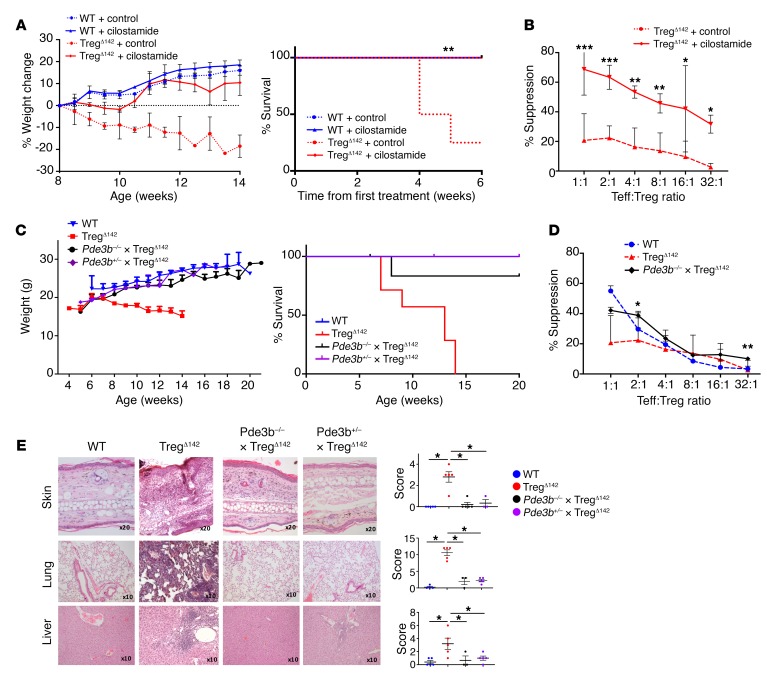
Figure 6. Pharmacological inhibition of PDE3B or genetic deletion of Pde3b reverses the lethality and phenotype of the autoimmune syndrome induced by Treg-specific loss of miR-142.
(A) Weight (left) and survival (right) of TregΔ142 and WT littermate control mice after 8 weeks of treatment with 6.4 mg/kg intraperitoneal cilostamide or control (n ≥ 3 for WT mice and n ≥ 6 for TregΔ142 mice). Loss of more than 15% of body weight was the predefined mortality endpoint. (B) Coculture Treg suppression assay after 4 weeks of cilostamide treatment. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, 1-way ANOVA. Data combined from 3 independent experiments. (C) Weight (left) and survival (right) of Pde3b–/– × TregΔ142, TregΔ142, Pde3b+/– × TregΔ142, and WT mice. n ≥ 5 (Pde3b–/– × TregΔ142); n ≥ 3 (Pde3b+/– × TregΔ142); n ≥ 7 (TregΔ142); and n ≥ 5 (WT mice). (D) Coculture Treg suppression assay comparing germline deletion of Pde3b (Pde3b–/– × TregΔ142) with TregΔ142 and WT littermate control mice. P values signify comparison between Pde3b–/– × TregΔ142 and TregΔ142. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, 1-way ANOVA. Data combined from 2 independent experiments. n ≥ 6. (E) H&E staining of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from ear skin, liver, and lung (left) with histological scoring as described in Methods (right). Original magnification, ×20 (ear skin); ×10 (liver and lung). *P < 0.05, Student’s t test. n = 5 (Pde3b–/– × TregΔ142, TregΔ142 and WT); n = 3 (Pde3b+/– × TregΔ142). WT and TregΔ142 skin, lung, and liver histology are also shown in Figure 3D.