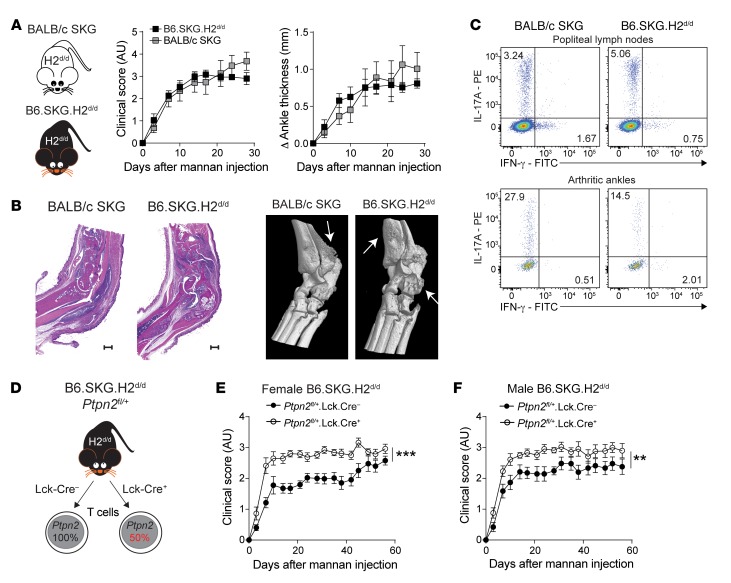
Figure 4. Ptpn2 haploinsufficiency promotes arthritis through T cells.
(A) Clinical score and ankle swelling in BALB/c SKG (n = 6) and B6.SKG.H2d/d (n = 6) mice after injection of mannan. (B) Representative H&E staining (left; scale bars: 500 μm) and representative micro-CT images (right) of arthritic ankles from BALB/c SKG and B6.SKG.H2d/d mice. Arrows indicate bone erosion or reactive bone deposition. (C) Representative flow cytometry staining of Th1 and Th17 in popliteal lymph nodes (top) and arthritic ankles (bottom) of BALB/c SKG and B6.SKG.H2d/d mice. (D) Generation of B6.SKG.H2d/d mice with a T cell–specific haploinsufficiency of Ptpn2. (E and F) Clinical score of mannan-induced arthritis in female (E) and male (F) B6.SKG.H2d/dPtpn2fl/+Lck-Cre– (female, n = 9; male, n = 9) and B6.SKG.H2d/dPtpn2fl/+Lck-Cre+ (female, n = 8; male, n = 9) mice. Compiled data from at least 2 independent experiments are presented. Arthritis severity was quantified using the area under the curve. Bars represent mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by Mann-Whitney.