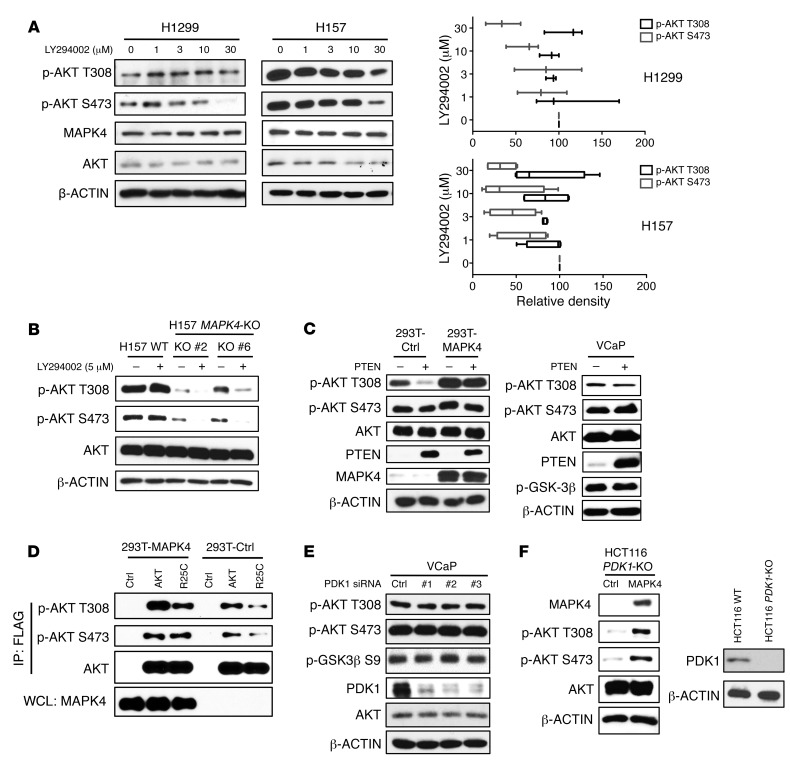
Figure 3. MAPK4 activates AKT independent of PI3K/PDK1.
(A) H1299 and H157 cells with high endogenous MAPK4 were treated with increasing doses of PI3K inhibitor LY294002 for 24 hours. Western blots were used to detect AKT phosphorylation. The phosphorylation of AKT at T308 and S473 was analyzed using ImageJ (33). The data are from 3 (for H1299 cells) and 4 (for H157 cells) independent studies. Box and whisker plots indicate average value with the box extending from the 25th to 75th percentiles and the whisker extending from Min to Max. (B) H157 and the H157 MAPK4-KO cells (KO clone 2 and KO clone 6) were treated with 5 μM LY294002 for 2 hours. Western blots were used to detect AKT phosphorylation. (C) PTEN was ectopically overexpressed in HEK293T cells overexpressing control (293T-Ctrl) or MAPK4 (293T-MAPK4), as well as in VCaP cells. Western blots were used to detect AKT phosphorylation and confirm PTEN overexpression. (D) The FLAG-tagged AKT1 and AKT1R25C mutants were overexpressed in HEK293T-Ctrl and HEK293T-MAPK4 cells. After immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG M2 affinity gel, phosphorylation of the overexpressed AKT1 was detected with Western blots. WCL: whole-cell lysate. (E) Three independent siRNAs against PDK1 were used to knock down PDK1 expression in VCaP cells. Western blots were used to detect AKT phosphorylation and confirm knockdown of PDK1. (F) Left, MAPK4 was ectopically overexpressed in the HCT116 PDK1-KO cells. Western blots were used to detect AKT phosphorylation. Right, Western blots were used to confirm loss of PDK1 expression in the HCT116 PDK1-KO cells. Ctrl: control. Data are representative of at least 3 independent experiments.