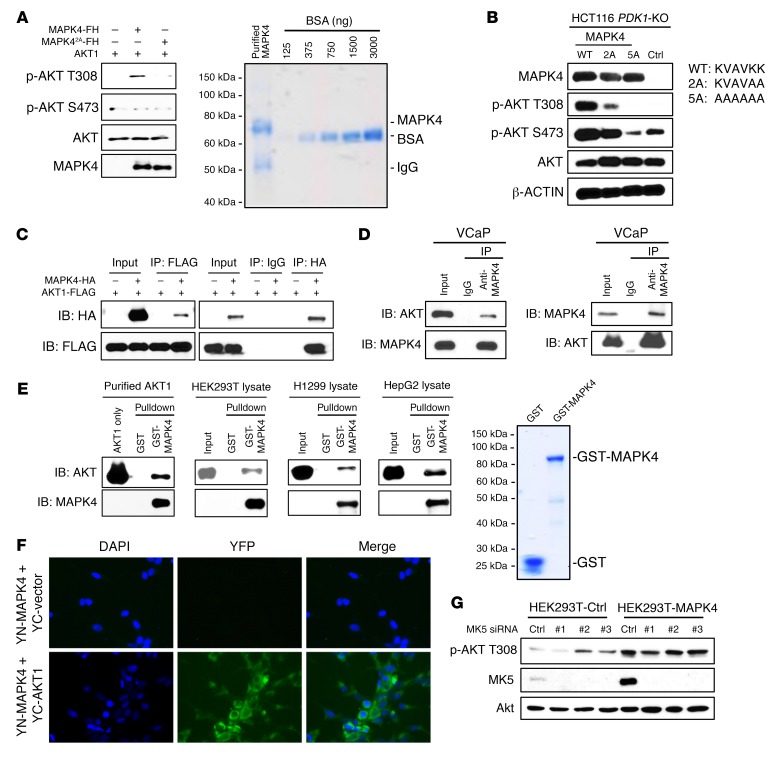
Figure 4. MAPK4 interacts with AKT and is a novel T308 kinase.
(A) FLAG/His-tagged MAPK4 and the MAPK42A mutant were overexpressed in PNT1A cells and purified using Ni-NTA column followed by immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG M2 affinity gel. In vitro kinase assay was performed using a commercially available recombinant AKT1. AKT phosphorylation was detected by Western blots. MAPK42A carries KVAVAA in place of the KVAVKK ATP binding motif. Coomassie blue staining reveals that the purified FLAG/His-tagged MAPK4 (with a calculated molecular weight of 69.6 kDa) contains one major band around 70 kDa. F/H: 2× FLAG and 10× His tag. (B) MAPK4 and the MAPK42A and MAPK45A mutants were overexpressed in HCT116 PDK1-KO cells. AKT phosphorylation was detected by Western blots. MAPK45A carries AAAAAA in place of the KVAVKK ATP binding motif. Coimmunoprecipitation (co-IP) assays reveal (C) ectopically overexpressed AKT1 binding to ectopically overexpressed MAPK4 in HEK293T cells, and (D) endogenous AKT1 binding to endogenous MAPK4 in VCaP cells. (E) Pull-down assay on the binding between purified GST-MAPK4 protein and purified AKT1 as well as endogenous AKT in the HEK293T, H1299, and HepG2 cell lysates. GST was used as control. GST-MAPK4 and GST were overexpressed in E. coli and purified using the glutathione sepharose beads. Coomassie blue staining confirms major bands of around 90 kDa and 26 kDa in the purified GST-MAPK4 and GST, respectively. (F) BiFC assay for AKT association with MAPK4 in cytoplasm. Hela cells were cotransfected with YN-MAPK4 and YC-AKT1 or YC control vectors. Forty-eight hours later, the cells were fixed, counterstained with DAPI, and imaged for YFP fluorescence to indicate MAPK4-AKT1 interaction. Original magnification: ×400. (G) Three different MK5 siRNAs were transfected into control and MAPK4-overexpressing HEK293T cells. Western blots were used to confirm MK5 knockdown and compare AKT phosphorylation. Ctrl: control. Data are representative of at least 3 independent experiments.