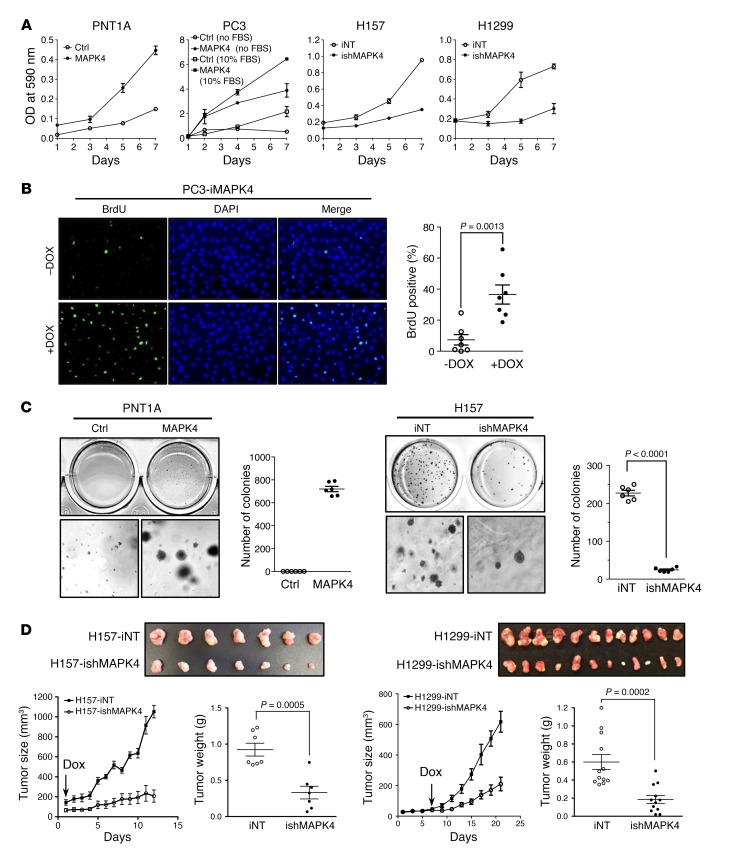
Figure 8. MAPK4 induces oncogenic outcomes.
(A) MTT assays comparing the proliferation of the control (Ctrl) and MAPK4-overexpressing PNT1A cells, the control and MAPK4-overexpresssing PC3 cells cultured in 10% FBS (open and filled squares) and in serum-free media (open and filled circles), the H157 cells with 4 μg/ml Dox-induced knockdown of MAPK4 (ishMAPK4) and control (iNT), and the H1299 cells with 4 μg/ml Dox-induced knockdown of MAPK4 and control. Data are mean ± SD. (B) BrdU incorporation assay comparing the cell proliferation of the PC3-iMAPK4 cells with (+) and without (–) Dox induction. Data are mean ± SEM. P value by unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test. (C) Soft agar assays comparing the anchorage-independent growth of the control and MAPK4-overexpressing PNT1A cells (left panels) and the H157 cells with 4 μg/ml Dox-induced knockdown of MAPK4 and control (right panels). Higher magnifications are shown in the bottom panels. Original magnification: ×50. Also shown are the quantification of colony numbers. Data are mean ± SEM. P value by unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test. (D) Dox-inducible knockdown of MAPK4 significantly delays tumor progression of H157 and H1299 xenografts in SCID mice. A quantity of 1 × 106 iNT or ishMAPK4 cells were s.c. injected into the lateral flanks of SCID mice (iNT: left side; ishMAPK4: right side). Mice began receiving 2 mg/ml Dox and 10% sucrose in drinking water as indicated by the arrow. Tumors were harvested as indicated. Ctrl: control; iNT: Dox-inducible nontargeting control; ishMAPK4: Dox-inducible knockdown of MAPK4. Data are mean ± SEM. P values by unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test. Data are representative of at least 3 independent experiments.