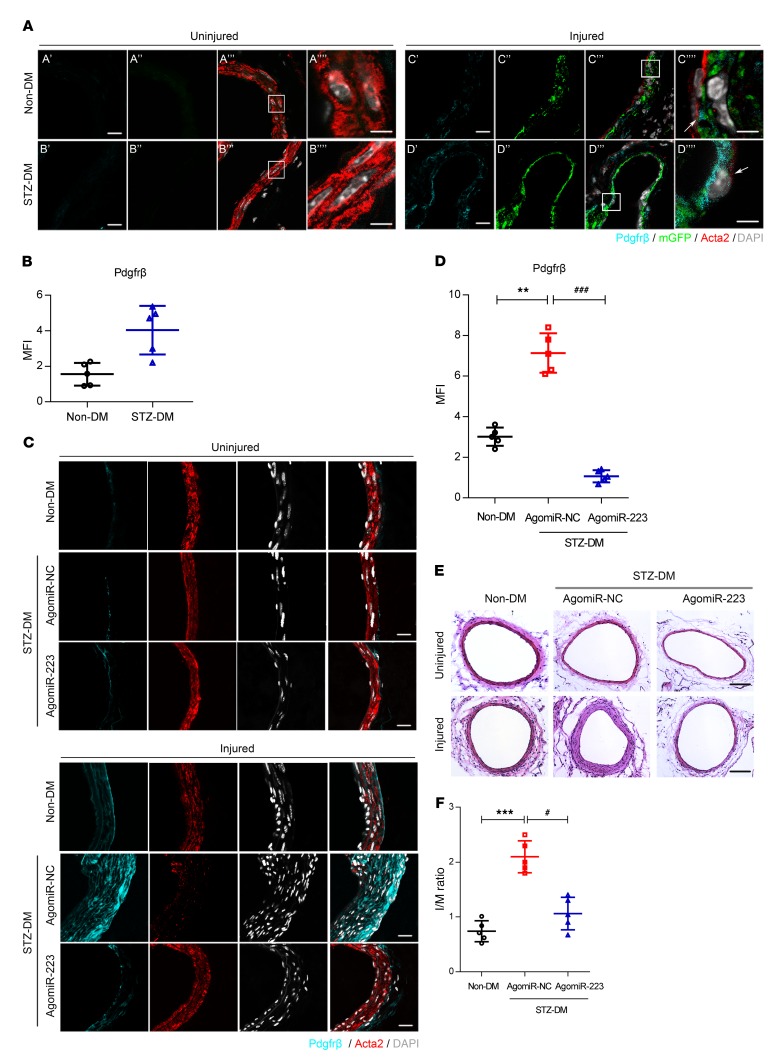
Figure 6. Platelet-derived miR-223 is responsible for inhibition of neointima formation in diabetic mice after femoral artery wire injury.
(A) Representative images of Pdgfrβ expression in uninjured and injured femoral arteries of PF4-cre:mT/mG mice under non-DM or STZ-DM conditions (n = 5). The injured femoral arteries were harvested on the seventh day after injury. Scale bars: 20 μm. (B) Quantification of Pdgfrβ expression in mGFP-positive VSMCs in the injured femoral arteries (n = 5). Data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 vs. non-DM. (C) Representative immunofluorescence of Pdgfrβ in uninjured or injured femoral arteries from non-DM mice and STZ-DM mice treated with AgomiR-NC or AgomiR-223 at 4 weeks after wire injury (n = 5). Green, Pdgfrβ; blue, DAPI that reflects total cells; red, Acta2 in VSMCs. Scale bars: 20 μm. (D) Quantification of Pdgfrβ expression in VSMCs in the injured femoral arteries (n = 5). Data are presented as mean ± SD. **P < 0.01 vs. non-DM; ###P < 0.001 vs. STZ-DM mice treated with AgomiR-NC. (E) H&E staining of serial cross sections from femoral arteries from non-DM mice and STZ-DM mice treated with AgomiR-NC or AgomiR-223 at 4 weeks after injury (n = 5). Scale bars: 100 μm. (F) Morphometric measurements of I/M ratio in the injured femoral arterial sections (n = 5). Data are presented as mean ± SD of I/M ratio. ***P < 0.001 vs. non-DM; #P < 0.05 vs. STZ-DM mice treated with AgomiR-NC. Statistical significance was determined using parametric t test (B) and 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer multiple-comparisons test (D and F).