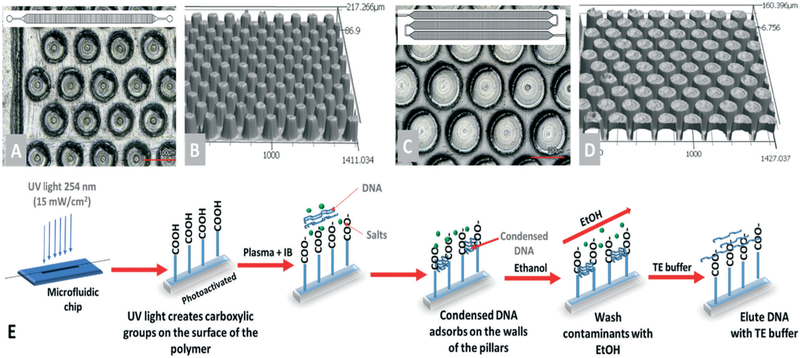
Fig. 2.
Microfluidic devices used for μSPE of cfDNA. (A) Top view of the pillars in the 1-bed device in which the bed length was 24 mm, and bed width was 1.4 mm. (B) Profile image of a section of the pillared channel of the 1-bed chip. (C) View of the 3-bed design: 34 mm bed length with a 1.7 mm width. (D) A profile image of the pillars in the 3-bed device. (E) General workflow for the cfDNA extraction from the plasma inside the microfluidic device. Prior to injection, samples were digested with proteinase K, protein/peptide clearance with magnetic particles, and then mixed with IB. In the device, the condensed DNA adsorbs onto the μSPE surfaces, washed using 70% EtOH, and then dried before elution with a low ionic strength buffer.