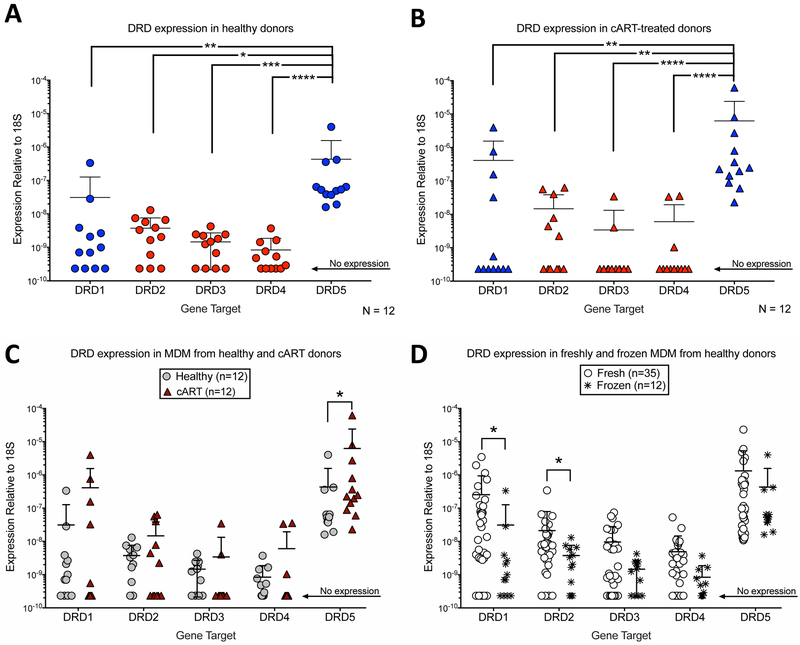
Figure 5:
RNA from human MDM isolated from previously frozen PBMC was collected from 12 healthy, and 12 cART-treated donors to quantify expression of DRD1, DRD2, DRD3, DRD4, and DRD5. Expression level of each receptor is normalized to the level of the endogenous control 18s (ΔCT), and data is represented as the transformed value 2−ΔCT. (A, B) Healthy and cART donor MDMs isolated from previously frozen PBMC express significantly greater levels of DRD5 than any other receptor. Significance was determined via Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test, (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, p<.001 ***, p<0001****). (C) In MDM isolated from previously frozen PBMC, cART donors express significantly greater DRD5 than healthy donors. Significance was determined via individual unpaired Mann-Whitney tests between healthy and cART groups for each dopamine-receptor subtype. There was no significant difference in expression for any other dopamine-receptor subtype (*p<0.05). (D) Across all healthy donors, MDM isolated from previously frozen PBMC express less DRD1 and DRD2 than freshly isolated MDM. Significance was determined via individual unpaired Mann-Whitney tests between fresh and frozen groups for each dopamine-receptor subtype. There was no significant difference in expression for other dopamine-receptor subtype (*p<0.05).