Fig. 7. AEA inhibits p-CREB signaling and BCRP promoter binding in BeWo cells.
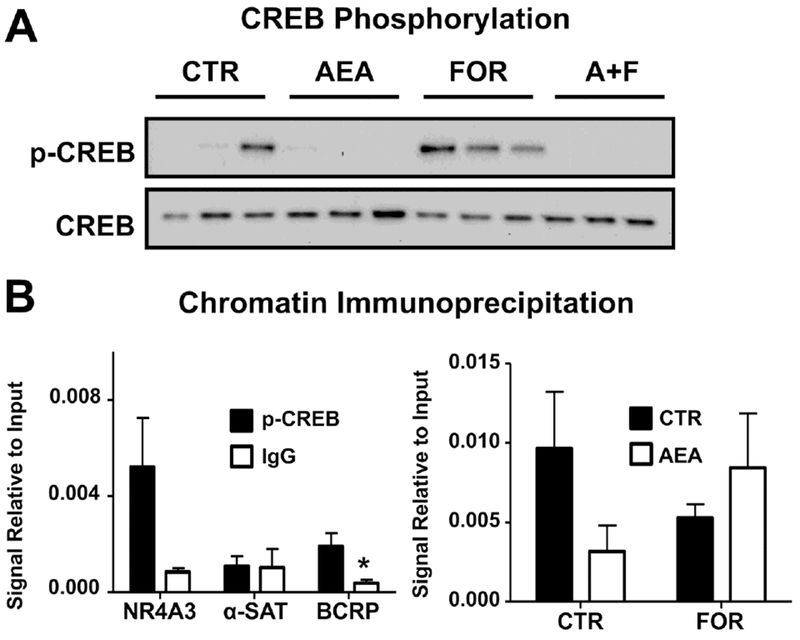
A. Western blot of p-CREB signaling in AEA- and FOR-treated cells. Lysates were prepared from BeWo cells treated for 1 h with AEA (10 μM), FOR (50 μM), or both, and analyzed for p-CREB and CREB (37 kDa) by Western blot. B. Validation of chromatin immunoprecipitation. ChIP was performed on untreated cells using a p-CREB antibody (black bars) or an IgG control (white bars), and samples were analyzed by qPCR for NR4A3, a positive control for p-CREB ChIP, α-satellites, a negative control, and the unique BCRP cAMP response element sequence. Data are presented as mean ± SE (n = 3-4). C. ChIP analysis of p-CREB binding to the BCRP promoter region. BeWo cells treated for 1 h with AEA (10 μM), FOR (50 μM), or both. ChIP was performed using a p-CREB antibody and samples were analyzed by qPCR for the unique BCRP cAMP response element sequence. Data are presented as mean ± SE (n = 3-5). Ct values for each sample were compared against respective 2% input controls. Asterisks (*) represent statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) compared to p-CREB precipitated samples.
