Figure 5.
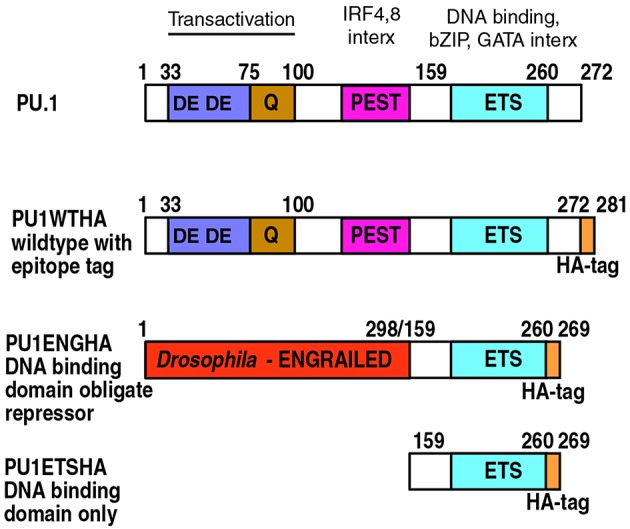
PU.1 structure and derivatives of PU.1 used for functional analysis. Domain boundaries within the amino acid sequence of murine PU.1 are depicted with their associated functions indicated at the top (4, 18, 90, 91). Epitope-tagged wildtype PU.1 (PU1WTHA) and two epitope-tagged, modified constructs are shown (PU1ENGHA, PU1ETSHA); these are used to interrupt endogenous PU.1 activity (79, 82). PU1ENGHA and PU1ETSHA have a full DNA binding domain and efficiently enter open chromatin, but are deficient in entering closed chromatin (85). DE: Acidic residue-rich transactivation domain. Q: Glutamine-rich transactivation domain. PEST: Proline, Glutamate, Serine and Threonine-rich domain, site of IRF4 and IRF8 interaction (interx). Note that in PU.1 this “PEST” domain does not make the protein unstable. ETS: E-twenty-six proto-oncogene homology domain, the DNA binding domain of PU.1. This is also the region that interacts with basic leucine zipper (bZIP) factors such as Jun and C/EBP factors, and GATA family factors.
