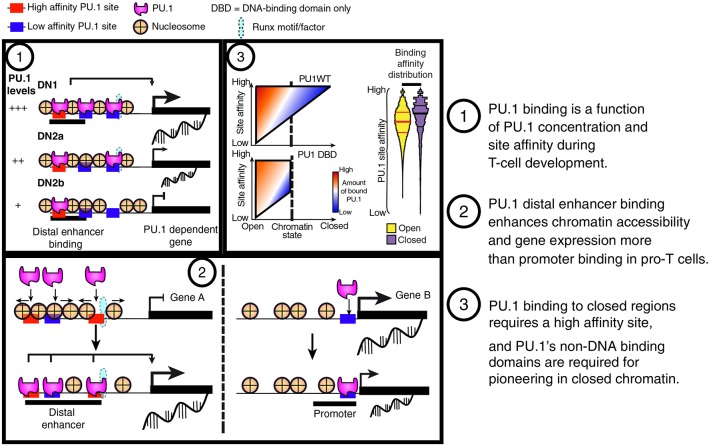
Figure 6.
Summary of PU.1 binding features in pro-T cells. (1) PU.1 binding is preferentially retained at high-affinity sites as pro-T cells progressively reduce their PU.1 levels. This feature indicates that PU.1 primarily uses mass action (concentration × affinity) to determine its genomic site choices in these cells. (2) PU.1 works as a positive regulator in pro-T cells primarily by binding and controlling accessibility of sites distal to the transcriptional start sites, not at promoters. (3) The binding profiles of full-length PU.1 (PU1WT) show a tradeoff between binding site affinity and binding site accessibility in chromatin; however, constructs with the PU.1 DNA binding domain but lacking the transactivation domains (PU1 DBD) are poor at engaging sites in closed chromatin no matter how high their potential affinities.