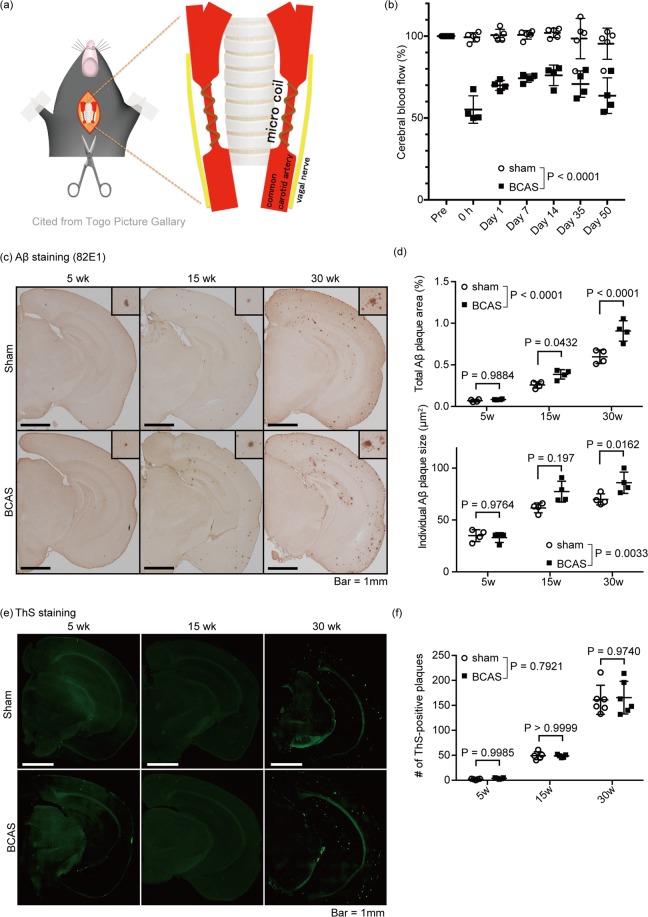
Figure 1.
BCAS accelerated Aβ plaque growth in APP/PS1 mice. (a) Schema of the BCAS method. Microcoil was introduced into the common carotid artery, avoiding the vagal nerve. (b) Temporal profiles of cerebral blood flow in sham- and BCAS-operated mice. (c,e) Immunohistochemical detection of Aβ in the brain of sham- and BCAS-operated mice. Mice were sacrificed at week 5, 15 or 30 after the surgery. Representative immunohistochemical images are shown from a total of n = 4 mice. Insets are magnified view of Aβ plaques. Bar = 1 mm. (d) Quantification of panels (c). Total Aβ plaque area and individual Aβ plaque area are measured. Mean ± SD. n = 4 per group. (e) Fluorescent images of Thioflavin-S staining visualization of the Aβ-plaque core. Representative immunohistochemical images are shown from a total of n = 5 (week 5 and 15) or 6 (week 30) mice. (f) Quantification of panels (e), showing the number of Aβ plaques. Mean ± SD. n = 5 (week 5 and 15) or 6 (week 30) per group. Statistical significance was determined using Two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Sidak method.