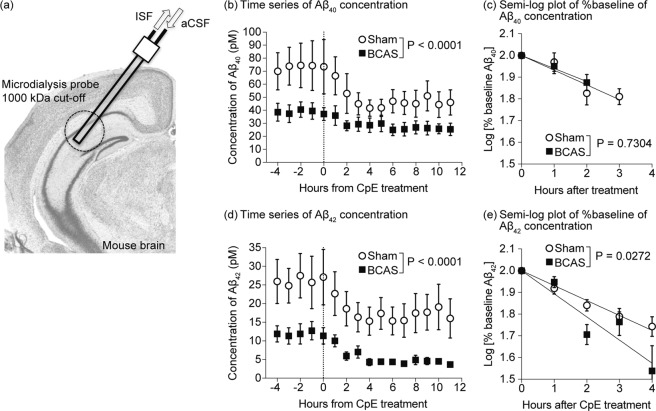
Figure 3.
BCAS decreased the concentrations of small molecular weight Aβ, and accelerated their apparent clearance in APP/PS1 mice. (a) Schematic view of the in vivo microdialysis apparatus. The guide cannula was stereotactically implanted into the hippocampus. The microdialysis probe, equipped with 1000 kDa semipermeable membrane, was inserted into the target region through the guide cannula. Artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF) was circulated within the probe every hour and collected as interstitial fluid (ISF). Aβ concentration was measured by ELISA. (b,d) Time-series of the Aβ40 and Aβ42 concentration in each fraction. A gamma-secretase inhibitor, Compound E, was administered at the time point 0 to inhibit the local production of Aβ. (c,e) Half-life periods of Aβ40 (c) and Aβ42 (e) within the hippocampus of sham or BCAS-operated mice. The concentrations from 0 h to 4 h in panels b and d were replotted and normalized with baseline concentration. Half-life periods of Aβ1–40 and Aβ1–42 were determined as the slopes of the concentrations. Statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA.