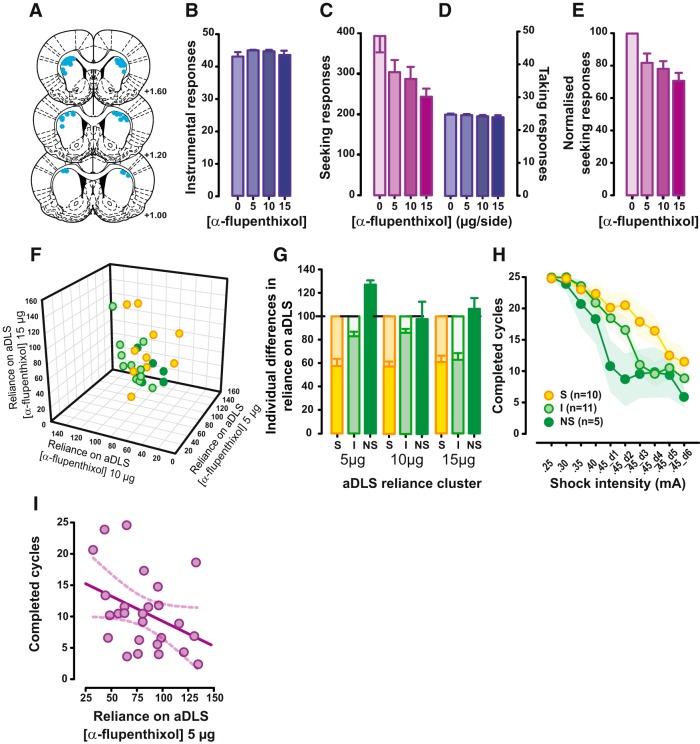
Figure 2.
Reliance on aDLS dopaminergic mechanisms of well established alcohol seeking predicts the vulnerability to compulsivity. A, The 26 rats included in the study all had injection sites (blue dots) located within the aDLS as verified by histological assessment of coronal sections from +1.6 to +1.0 mm anteroposterior from bregma. B, Early instrumental performance for 10% EtOH (purple bars) was unaffected by aDLS dopamine receptor blockade with α-flupenthixol (0, 5, 10, or 15 μg/side, n = 26). C, D, With the progression of training, while taking responses were never affected by aDLS dopamine receptor blockade (D, purple bars, on the right), seeking responses were dose-dependently decreased by bilateral aDLS infusions of the dopamine receptor antagonist α-flupenthixol (0, 5, 10, or 15 μg/side, n = 26; C, fuchsia bars, on the left). E, Marked individual differences in the susceptibility of alcohol-seeking responses to aDLS dopamine were revealed when normalizing the influence of aDLS dopamine receptor blockade on seeking responses relative to baseline performance (i.e., the vehicle-treated rats were considered our controls, and their responses were normalized to 100%, whereas the lever presses at each dose tested were then expressed as percentage changes from vehicle). F, G, A cluster analysis segregated rats that were highly susceptible to (S rats, n = 10; yellow), not affected by (NS rats, n = 5; green), and minimally affected by (I rats, n = 11; light green) aDLS dopamine receptor blockade. H, The susceptibility of alcohol seeking to aDLS dopamine predicted the vulnerability to subsequent development of compulsive alcohol seeking, as shown by the higher number of completed seeking–taking cycles per session under probabilistic punishment displayed by S rats (n = 10; yellow) compared with both NS rats (n = 5; green) and I rats (n = 11; light green). I, The relationship between susceptibility to aDLS dopamine receptor blockade and the emergence of compulsive alcohol seeking was further supported by dimensional analysis (Pearson's correlation). Graphs show the mean ± SEM.