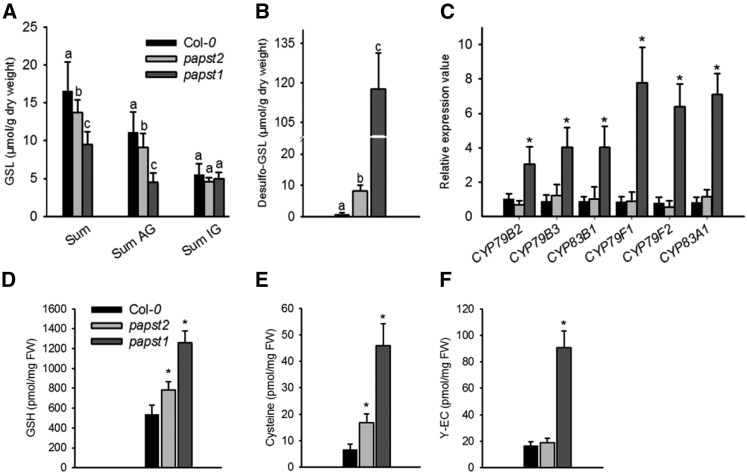
Figure 6.
Glucosinolate Biosynthesis and Sulfate Assimilation Are Slightly Affected in papst2.
(A) Glucosinolate contents (µmol/mg dry weight) in papst2 plants relative to wild-type plants (Col-0) and the papst1 T-DNA insertion line.
(B) Desulfo-glucosinolates (µmol/mg dry weight) contents in papst2 compared with wild-type plants (Col-0) and the papst1 T-DNA insertion line.
AG = aliphatic glucosinolates; GSL = glucosinolates; IG = indolic glucosinolates.
The data are the sums of three independent biological replicates (independently grown plant trays), with GSLs isolated from six individual plants from each. Statistical analysis performed with ANOVA, Tukey’s test (Supplemental Data Set). Different letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05.
(C) Glucosinolate biosynthesis gene expression is affected in papst1 but not in the papst2 T-DNA insertion line.
Relative gene expression values are given compared with the wild type Col-0 = 1. Data show means ±sd, (n = 3). Asterisks indicate significant differences compared with the wild-type Col-0 (Student´s t test, P < 0.05).
(D-F) Glutathione = GSH (D), Cys (E), and γ-glutamylcysteine or γ-EC (F) levels were determined in 4-week-olds as described in Methods and were compared with those of papst1. The data are the sums of two independent experiments, with five biological replicates. Asterisk indicates significant difference compared with the wild type (Col-0; Student’s t test, P < 0.05). FW = fresh weight.