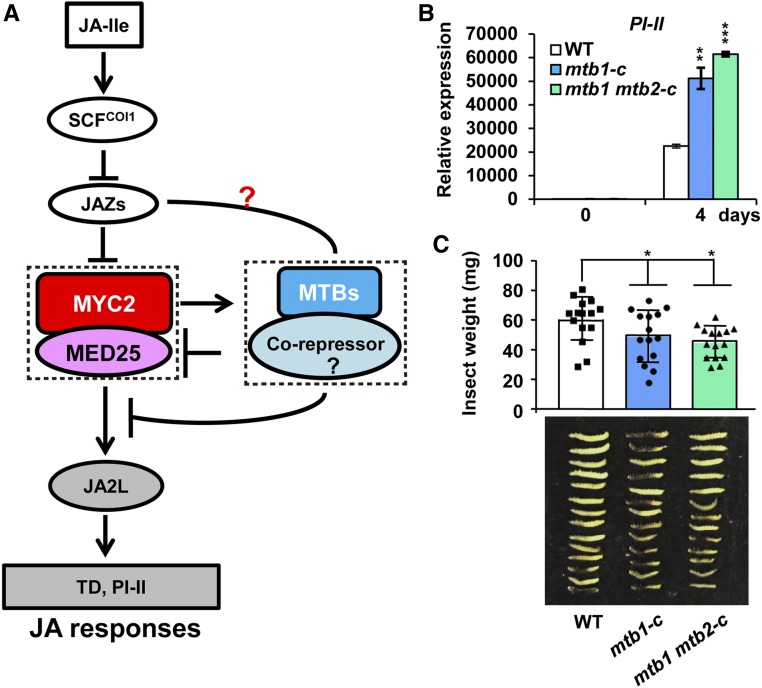
Figure 7.
MTB Genes Represent a Tool for Crop Protection.
(A) Proposed mechanism by which MYC2 and MTB proteins form a feedback loop to terminate JA signaling. MYC2 and MED25 activate the expression of MTB genes; in turn, MTB proteins interfere with the MED25-MYC2 interaction and DNA binding activity of MYC2 to terminate JA-triggered defense responses.
(B) Expression of PI-II in wild-type, mtb1-c, and mtb1 mtb2-c plants exposed to H. armigera larvae. Plants were harvested at the indicated time points during the feeding trial for RNA extraction and RT-qPCR analysis. Data represent means ± sd (n = 3). Asterisks indicate significant differences from the wild type according to Student’s t test at **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001
(C) Average weight (top) and images (bottom) of larvae recovered at the end of day 4 of the feeding trial using whole plants of the wild type, mtb1-c, and mtb1 mtb2-c. Data represent means ± sd (n = 15). Each symbol denotes the weight of an individual larva. Asterisks indicate significant differences from the wild type according to Student’s t test at *, P < 0.05 (Supplemental Data Set 2).