Fig. 1.
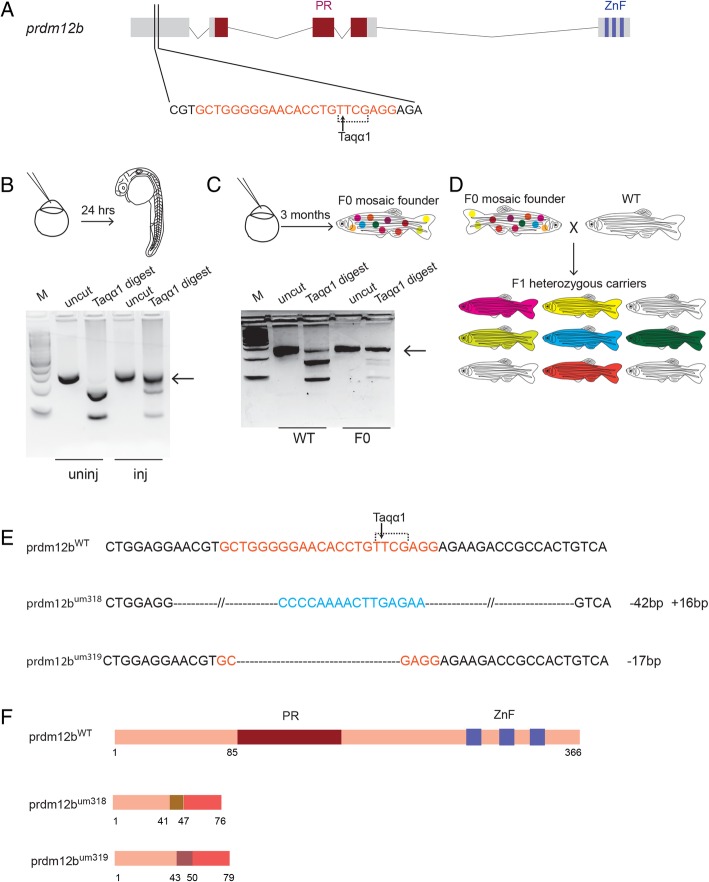
Generation of germ line prdm12b mutants. a. Schematic showing genomic sequence of prdm12b. Exons are indicated as boxes and black lines represent introns. The PR domain and three zinc fingers (ZnF) are highlighted in dark red and blue, respectively. The CRISPR target sequence is shown in red with the Taq α1 restriction site bracketed and the black arrow indicating the Taq α1 cut site. b. Identification of functional guide RNAs. sgRNA and cas9 mRNA was injected into 1-cell stage embryos. Injected embryos were raised to 24hpf and Taq α1 digestion of PCR amplicons from pools of embryos was used to identify CRISPR-induced mutations (black arrow). c. Identification of individual F0 founders. sgRNA/cas9 injected embryos were raised to adulthood and crossed to wildtype fish. Taq α1 digests of PCR amplicons from pools of embryos was used to identify F0 mosaic founders (black arrow). d. Identification of F1 animals. Adult F0 mosaic founders were out-crossed to wildtype fish and the F1 offspring raised to adulthood. Taq α1 digests of PCR amplicons from individual fin clip genomic DNA was used to identify heterozygous F1 animals. e. Sequencing of F1 genomic DNA revealed the transmission of two different mutant alleles (um318, um319). um318 carries a 42 base pair deletion (black dashes) and a 16 base pair insertion (blue), while um319 carries a 17 base pair deletion (black dashes). The CRISPR target sequence is shown in red. f. Predicted amino acid sequence of mutant alleles. The um318 peptide shares its first 41 amino acids, and the um319 peptide its first 43 amino acids, with wildtype Prdm12b. The two mutant peptides then utilize a different reading frame that terminates at a premature stop codon N-terminal to the conserved PR domain. Inj = sgRNA/Cas9-injected embryos, uninj = uninjected control embryos