Fig. 12.
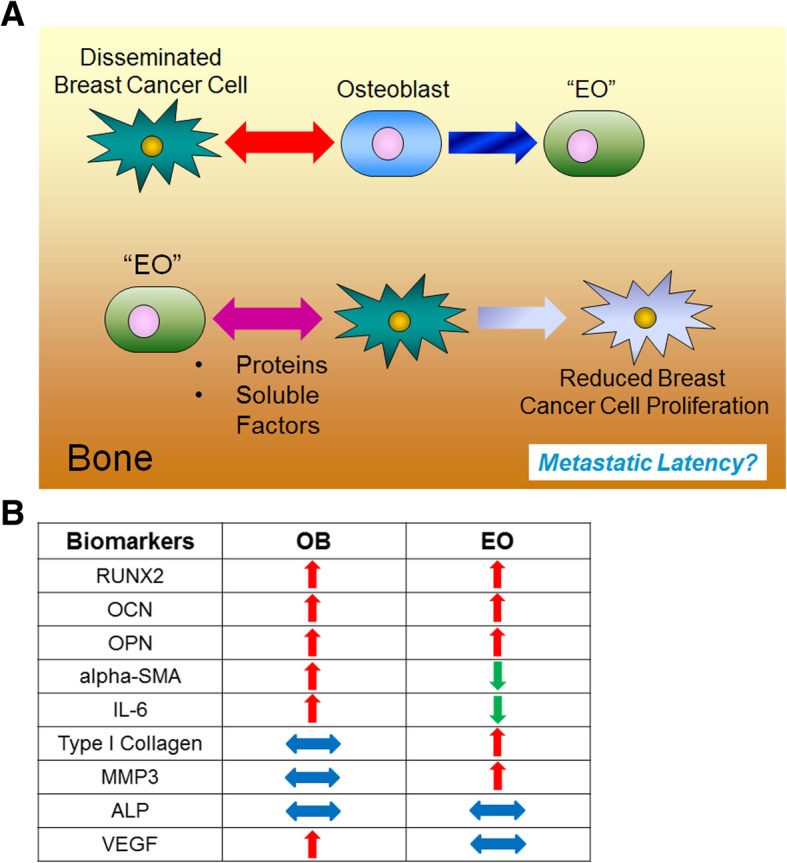
EO cells are distinct from “uneducated osteoblasts” and suppress breast cancer cell proliferation in the bone. a When disseminated breast cancer cells first enter the bone microenvironment, they engage in crosstalk with osteoblasts, leading to the generation of a subpopulation of osteoblasts defined as “educated osteoblasts.” “Educated osteoblasts,” in turn, engage in crosstalk with bone-disseminated breast cancers via proteins and soluble factors, among others, leading to a reduction in breast cancer cell proliferation in the bone microenvironment that may play a role in metastatic latency. b EO marker panel key: protein alterations in RUNX2, OCN, OPN, aSMA, IL-6, type I collagen, MMP3, ALP, and VEGF distinguish EOs from OBs. Red arrow indicates high protein expression, green arrow indicates low protein expression, and blue sideways arrow indicates average protein expression as determined by western blot and/or immunofluorescence
