Extended Data Figure 1. Known structures of CCR5 and CXCR4.
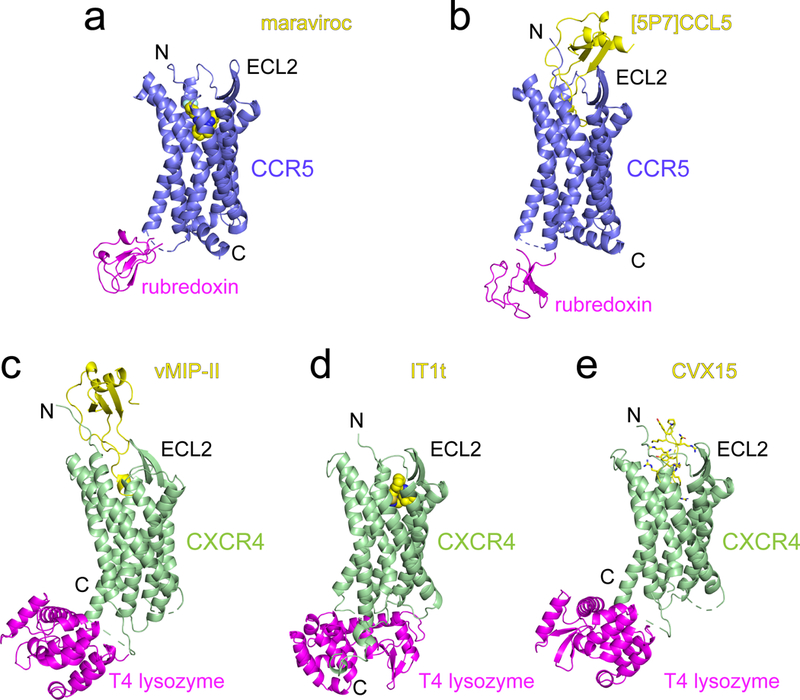
CCR5 and CXCR4 were identified as the coreceptors for HIV-1 entry in 199671-77. (a)-(b) Crystal structures of a modified CCR5 (ΔC224-N226→rubredoxin; ΔF320-L352; and point mutations C58Y, G163N, A233D, K303E) in complex with HIV entry inhibitor maraviroc (pdb ID: 4MBS; ref7) and a modified chemokine [5P7]CCL5 (an antagonist; pdb ID: 5UIW; ref10). CCR5 is shown in ribbon diagram in blue, the internally fused rubredoxin in magenta and the ligands in yellow. N-terminus (N), C-terminus (C) and the second extracellular loop (ECL2) are indicated. (c)-(e) Crystal structures of an engineered CXCR4 in complex with a viral chemokine antagonist vMIP-II (pdb ID: 4RWS; ref15), a small molecule antagonist IT1t (pdb ID: 3ODU; ref14) and a cyclic peptide antagonist CVX15 (pdb ID: 3OE0; ref14). CXCR4 is shown in green, the fused T4 lysozyme in magenta and the ligands in yellow. N, N-terminus; C, C-terminus; and ECL2, the second extracellular loop.
