Figure 5.
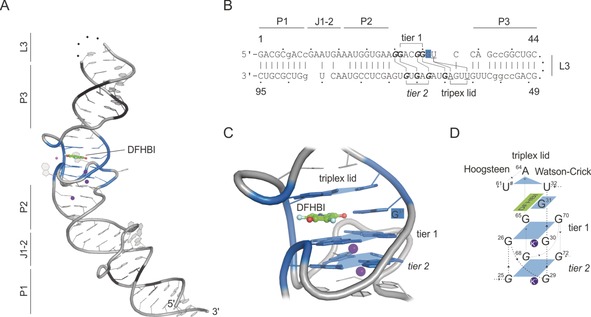
Spinach–DFHBI crystal structure (PDB ID: 4ts2).62 A) Crystal structure of Spinach; names of structural features are indicated. Black=substituted nucleotides for stabilization through Watson–Crick base pairs; Green=DFHBI, pink and purple spheres=Mg2+ and K+ ions; blue colored region=DFHBI‐binding region including G‐quadruplex; dotted line=cleavage site for crystal construct design (L3 loop region). B) Sequence of the crystallized Spinach sequence by Warner et al.62 Lower case=substituted nucleotides for stabilization through Watson–Crick base pairs; bold=G‐quadruplex forming nucleotides; underlined=triplex‐lid‐forming nucleotides. C) Close‐up view of the fluorogen‐binding region. G‐quadruplex tiers are shown, and shaped platforms are indicated by blue planes. Each plane coordinates a K+ ion (purple). DFHBI is shown in addition to its coordinating G31. The closing triplex lid is highlighted on top of DFHBI. D) Schematic overview of Spinach–DFHBI fluorogen‐binding region. Numbers indicate the nucleotide numbers from Spinach according to (B).
