Figure 1. IL-1β expression was significantly increased in both murine and human psoriatic lesions.
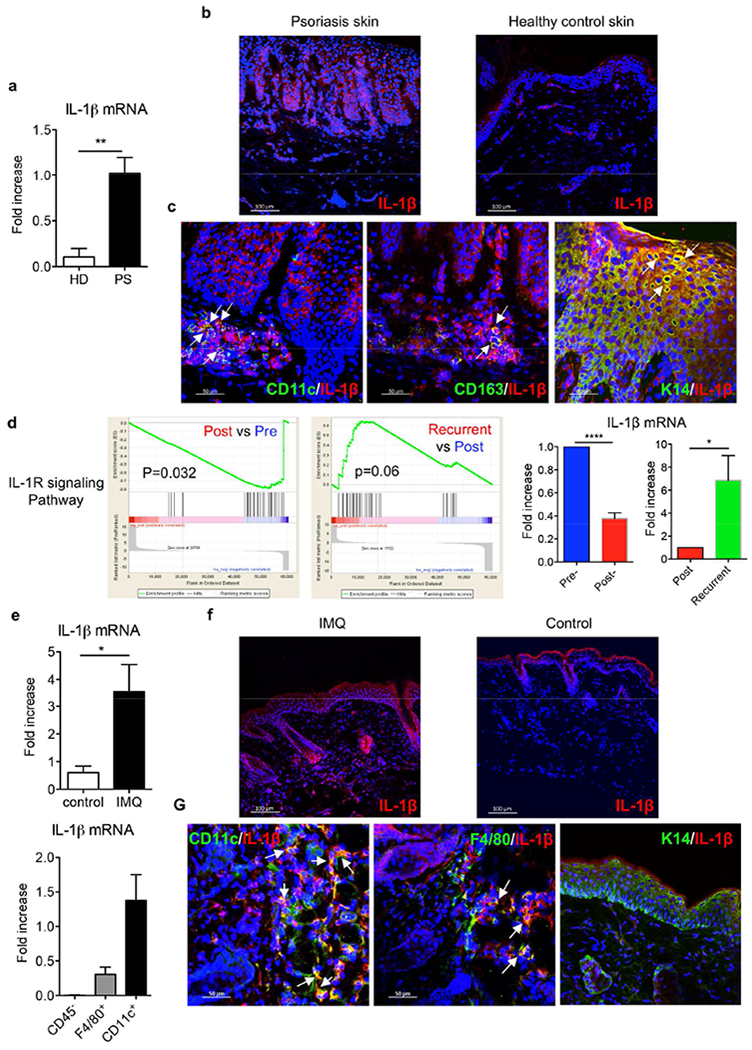
(a) IL-1β mRNA levels from skin biopsies collected from psoriasis patients (PS, n=5) and healthy donors (HD, n=4). (b) Frozen sections were stained with IL-1β mAb (red) and DAPI (blue). Scale bar =100 μm. (c) Frozen sections from psoriatic lesional skin were stained with IL-1β mAb (red) and human CD11c mAb (green) or human CD163 mAb (green) or keratin 14 mAb (green), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar =50 μm. (d) Gene set enrichment analysis identifies significant transcriptional downregulation of IL-1R signaling pathway in psoriasis patients initially effectively treated with glucocorticoid while upregulation in recurrent patients after stopping treatment (NCBI GEO with the accession number GSE114729). The mRNA expression of IL-1β by real-time PCR analysis was calculated using Pre- or Post-treatment level as base level. (e) C57BL/6 mice received daily topical application with IMQ or vehicle control for 3-5 days. IL-1β mRNA levels from IMQ-treated or vehicle control mouse skin were measured. CD11c+ cells, F4/80+ cells and CD45− cells were sorted from 3 days of IMQ-treated mouse skin and IL-1β mRNA level was measured. (f) Skin frozen sections from IMQ-or vehicle control-treated mice were stained with IL-1β mAb (red) and DAPI (blue). Scale bar =100 μm. (g) Skin frozen sections from IMQ-treated mice were stained with IL-1β mAb (red) and mouse CD11 c mAb (green), or mouse F4/80 mAb (green), or keratin 14 mAb (green), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar =50 μm. *p< 0.05, **p< 0.01, ***p< 0.001.
