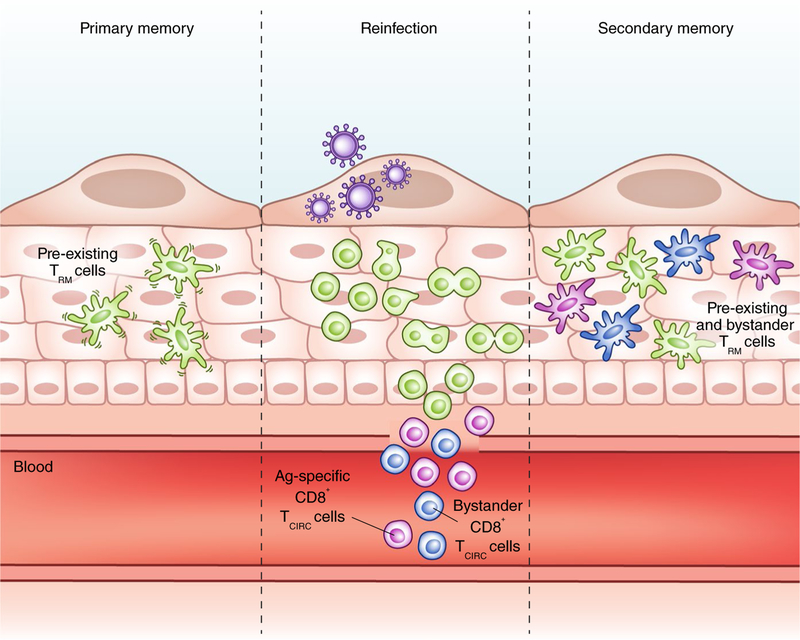
Fig. 1 |. Effects of secondary infection on a pre-existing TRM cell population.
CD8+ TRM cells (green) are motile sentinels that patrol and survey their tissue microenvironments for reinfection. When they recognize their target antigen (Ag) during reinfection, CD8+ TRM cells arrest and undergo in situ proliferation to generate a secondary pool of TRM cells that does not exit into the circulation. Antigen-specific (purple) and bystander (blue) CD8+ TCIRC cells are also recruited into the infected tissue and adopt long-term tissue residency without displacing the pre-existing TRM cells, thereby increasing the number and repertoire of TRM cells in the tissue. Credit: Marina Spence/Springer Nature