Figure 6. In Vivo Optical LTD of the MGN-LA Circuit Inhibits Cue-Induced Reinstatement.
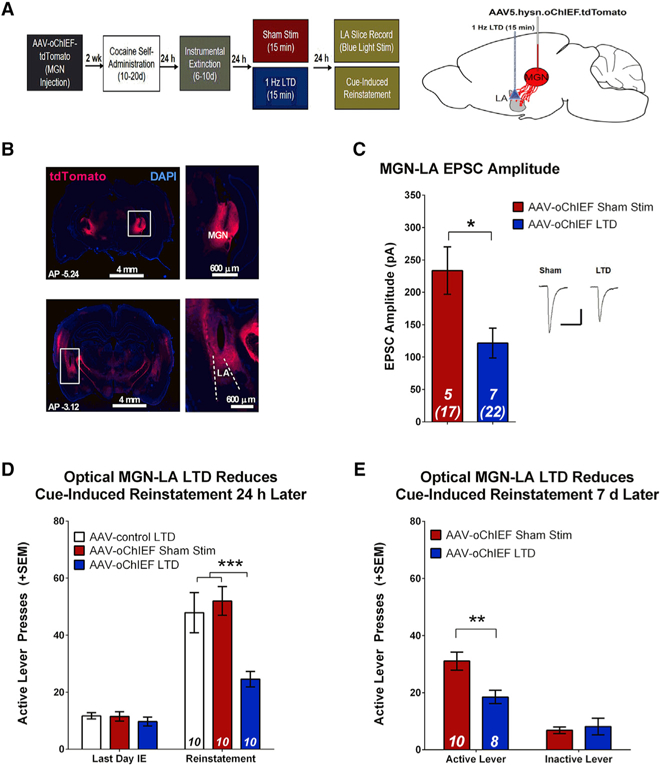
(A) Experimental design. oChIEF-expressing AAV5 was injected into the MGN, and optical fibers were implanted at the dorsal tip of the LA.
(B) Diagram and images demonstrating the position of virus injection in the MGN (top) and placement of optic fibers in the LA (bottom).
(C) In vivo dual hemisphere LTD of MGN-LA synapses attenuates EPSC amplitude relative to sham controls (unpaired t test, t(10) = 2.73, *p = 0.021). Inset, sample average EPSC traces evoked at Erev −70 mV; scale bars, 50 ms, 200 pA.
(D) In vivo dual hemisphere LTD of MGN-LA synapses attenuates reinstatement. There were no differences in active lever pressing between groups during the last day of IE. There is a significant reduction in active lever presses during reinstatement in rats that previously underwent optical LTD relative to animals that received a control virus and sham controls. Two-way ANOVA, main effect of group (F(2,27) = 7.04, p = 0.004) and a day x group interaction (F(2,29) = 8.08, p = 0.002); post hoc analysis: ***p < 0.001; error bars, mean x SEM; numbers in bars, number of rats.
(E) In vivo dual hemisphere LTD of MGN-LA synapses affects spontaneous recovery. 7 days after initial cue-induced reinstatement, rats underwent a second reinstatement test, revealing a significant reduction in active lever pressing in animals that previously underwent MGN-LA LTD relative to sham controls. Two-way ANOVA, main effect of group (F(1,32) = 5.04, p = 0.032), significant interaction (F(1,32) = 7.69, p = 0.009); post hoc analysis, **p < 0.01.
Error bars, mean ± SEM; numbers in italics, number of rats (number of neurons). See also Figure S5.
