FIG. 2:
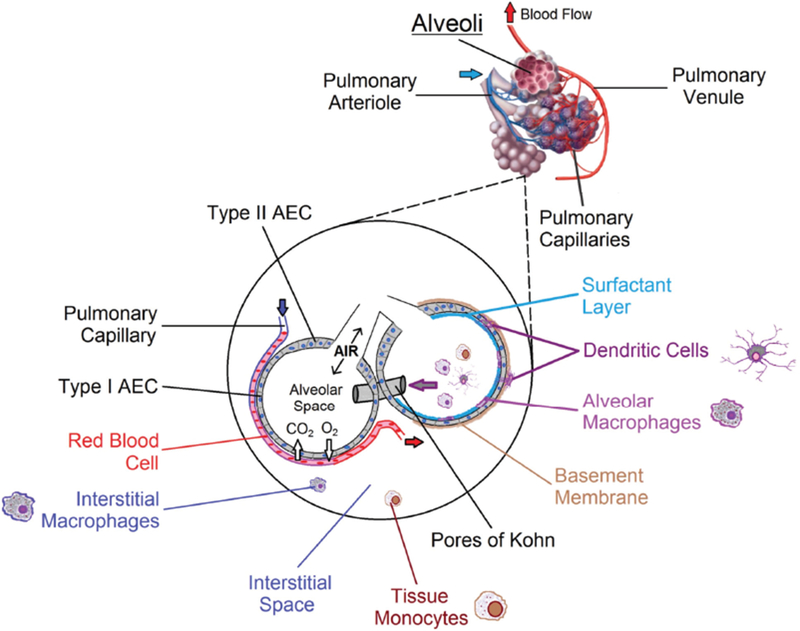
Human alveolar structure and cellular composition. At the alveolar level, oxygen diffuses into and carbon dioxide diffuses out of blood flowing through pulmonary capillaries. Inset: A wide variety of cell types are found in and around alveoli. Type I AECs make up the majority of the surface area involved in respiration. DCs are found embedded within the alveolar epithelium and just below it in the submucosa, from where they extend processes into the alveolar space to sample antigens. Immune cells transit between alveoli via pores of Kohn. Together, subsets of macrophages, dendritic cells, and tissue monocytes keep the airways clear of obstruction and direct interactions with cells of the adaptive immune system.
