Figure 1.
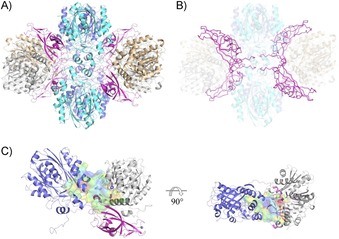
Structural analysis of PpATase. A) Structure of the heterododecamer Phl(A2C2)2B4 (PhlA=blue and cyan, PhlB=magenta, PhlC=gray and light brown). B) PhlB mediates the binding of two PhlA and two PhlC dimers. Two N‐terminal tails of PhlB (up to Arg28) are involved in tight interactions with adjacent PhlA and PhlC molecules as well as with the N‐terminal tail of a neighboring PhlB molecule. PhlB is shown in ribbon representation. C) The continuous cavity between PhlA, PhlB, and PhlC subunit trimer. The active site of PhlC (in violet, residues shown in stick representation) is situated adjacent to the cavity of PhlA. The long loop in PhlB (Glu74–Val87, magenta) is closing the cavity from the other side. The cavity is shown in surface representation (red/hydrophobic to blue/hydrophilic). See the Experimental Section for detailed descriptions.
