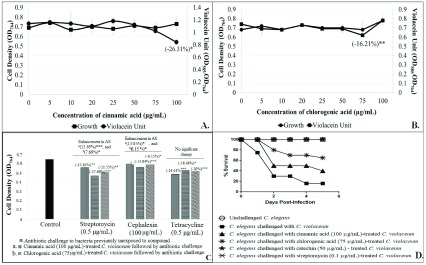
Figure 5. Effect of cinnamic acid and chlorogenic acid on C. violaceum.
‘Control’ in this figure is the vehicle control (0.5%v/v DMSO), which did not exert any effect on growth and violacein production of C. violaceum. ( A) Effect of cinnamic acid on growth and violacein production in C. violaceum. Bacterial growth was measured as OD 764; OD of violacein was measured at 585 nm, and Violacein Unit was calculated as the ratio OD 585/OD 764 (an indication of violacein production per unit of growth). ( B) Effect of chlorogenic acid on growth and violacein production in C. violaceum. Bacterial growth was measured as OD 764; OD of violacein was measured at 585 nm, and violacein unit was calculated as the ratio OD 585/OD 764 (an indication of violacein production per unit of growth). ( C) Pre-treatment of C. violaceum with chlorogenic acid and cinnamic acid enhances its susceptibility to streptomycin and cephalexin. ( D) Cinnamic acid, chlorogenic acid, and catechin reduced virulence of C. violaceum towards C. elegans. Catechin (50 μg/ml) and ampicillin (500 μg/ml) employed as positive controls conferred 100% protection on worm population. DMSO present in the ‘vehicle control’ at 0.5%v/v did not affect virulence of the bacterium towards C. elegans; DMSO (0.5%v/v) and compounds at tested concentrations showed no toxicity towards the worm. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001. AS, antibiotic susceptibility; QS, quorum sensing.