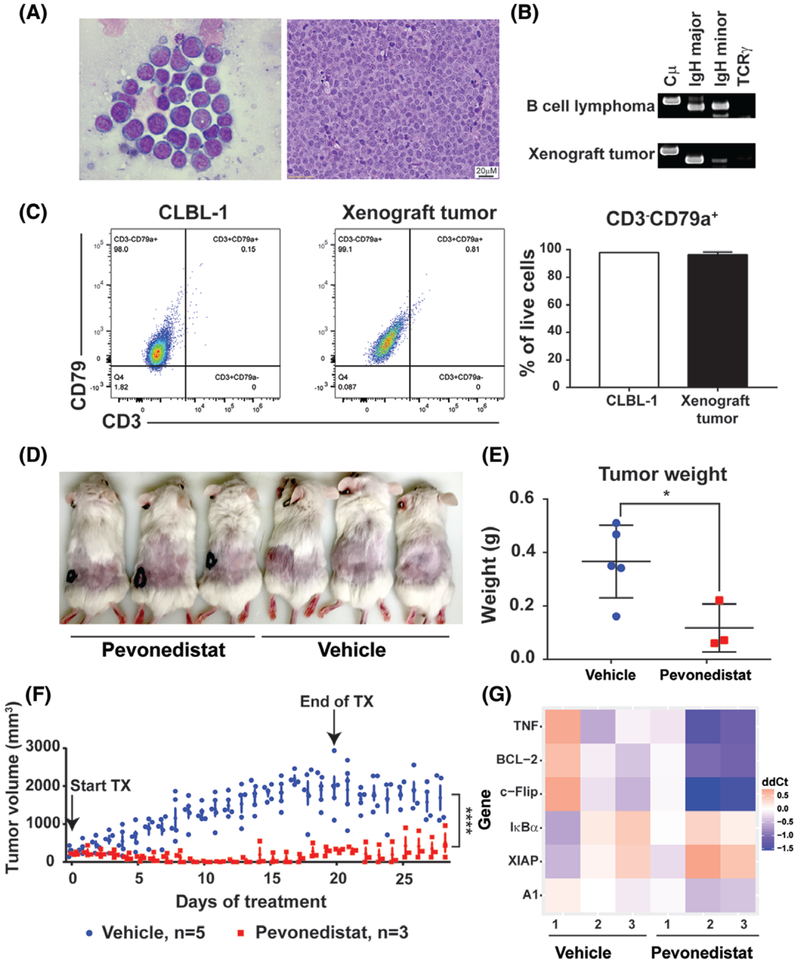
FIGURE 6.
Pevonedistat treatment leads to xenograft tumour regression. A-C, canine DLBCL murine xenograft tumour recapitulates canine large B-cell lymphoma in cell morphology, immunophenotype and cell surface expression markers. A, Cytologic and histologic analyses of xenograft tumour. B, PARR assay of xenograft tumour cells. Canine B-cell lymphoma sample was used as a positive control. C, Flow cytometry analysis and quantification of xenograft tumour cells and CLBL-1 cells. D, Representative image of xenograft mice with and without pevonedistat treatments. E, Tumour weight of vehicle and pevonedistat-treated mice. F, Tumour volume of vehicle and pevonedistat-treated mice. Arrows indicated the start of and the end of treatments. G, NF-κB pathway target gene expressions in xenograft tumours. After xenograft tumour formed, mice were treated with one dose of pevonedistat (60 mg/kg) (n = 3) or with one dose of vehicle (n = 3). Xenograft tumours were harvested 48 hours post-treatment. *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001. Data were presented as mean ± SD