Figure 2.
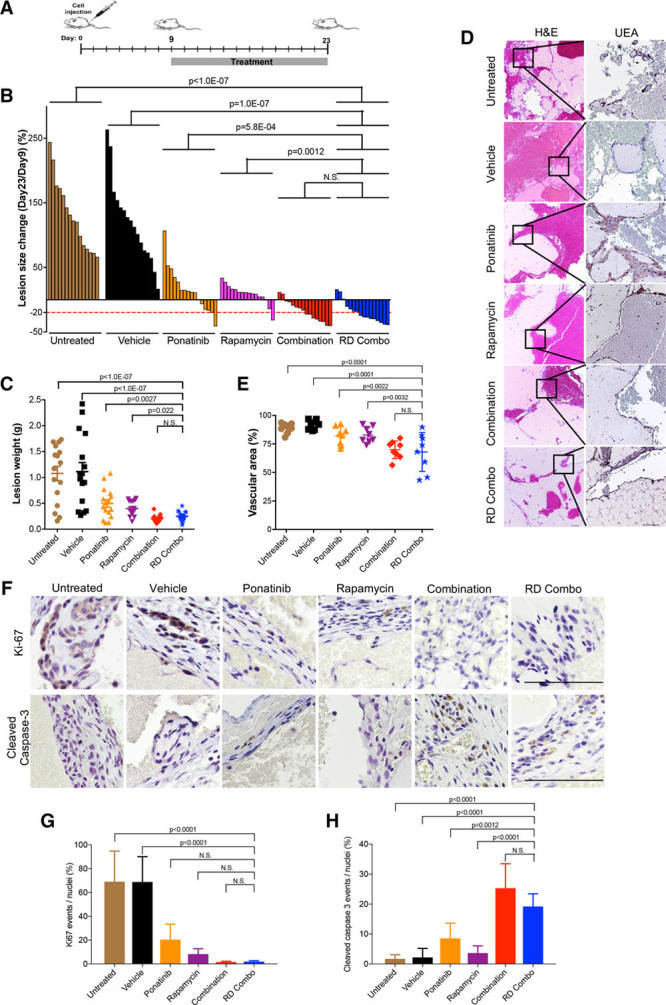
Ponatinib combined with rapamycin induces regression of murine venous malformation (VM). A, Treatment scheme: Human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC)-TIE2-L914F were injected into mouse at day 0 and lesions expanded until their size reached 110 mm2. Treatment was started (day 9) by daily oral gavage with vehicle, ponatinib (30 mg/kg), rapamycin (2 mg/kg), combination (ponatinib 30 mg/kg + rapamycin 2 mg/kg) and reduced-dose combination (RD combo, ponatinib 20 mg/kg + rapamycin 1 mg/kg) for 14 d. B, Waterfall plot of % lesion size change (day 23/day 9). Data expressed as single value for each lesion, linear mixed-effect model (n=8 mice with 2 lesions/group). C, Lesion weight: Data expressed as single value for each lesion, mean shown by horizontal bars, linear mixed-effect model (n=8 mice with 2 lesions/group). D, Representative Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) and UEA (Ulex europaeus agglutinin I) stained lesion sections. Scale bar: 100 μm. E, Quantification of vascular area. Data expressed as average value for 2 lesions on each mouse, mean shown by horizontal bars, 1-way ANOVA for multiple comparisons (n=8 mice with 2 lesions/group). F, Representative images of lesion sections stained with cleaved caspase-3 and Ki-67. Scale bar: 500 μm. G, Quantification of Ki-67 events and (H) quantification of cleaved caspase-3 events. Data expressed as mean±SD, 1-way ANOVA for multiple comparisons (n=5).
