Figure 3.
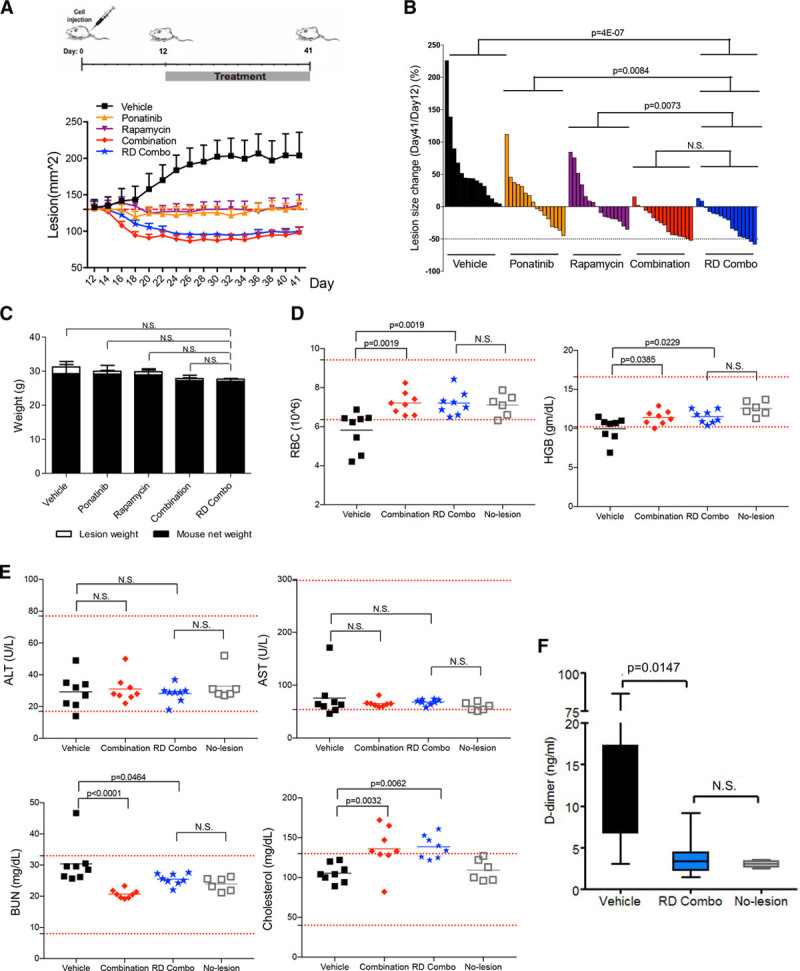
Long-term combination treatment with ponatinib and rapamycin (4 wk) shows minimal side effects in mice bearing venous malformation (VM). A, Treatment scheme: Human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC)-TIE2-L914F were injected into mouse at day 0 and lesions expanded until their size reached 130 mm2. Treatment was started (day 12) by daily oral gavage with vehicle, ponatinib (30 mg/kg), rapamycin (2 mg/kg), combination (ponatinib 30 mg/kg + rapamycin 2 mg/kg), and reduced-dose combination (RD combo, ponatinib 20 mg/kg + rapamycin 1 mg/kg) for 4 wk. Lesion size of each group measured every other day. Data expressed as mean±SEM. B, Waterfall plot of % lesion size change (day 41/day 12). Data expressed as single value for each lesion, linear mixed-effect model (n=8 mice with 2 lesions/group). C, Mouse body weight at day 41. Data expressed as mean±SD, 1-way ANOVA for multiple comparisons (n=6–8 mice/group). D and E, Analysis of red blood cells (RBC), hemoglobin (HBG), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in the peripheral blood of vehicle, combination, RD combo, and no lesion mouse groups. Red dashed lines indicated reference value and gray square-holes show values in mice without VM lesions (unchallenged, no cell injection). Data expressed as single value for each mouse, mean shown by horizontal bars, 1-way ANOVA for multiple comparisons (n=6–8 mice/group). F, D-dimer levels were tested in vehicle, RD combo, and no lesion group. Data expressed as mean±SD, 1-way ANOVA for multiple comparisons (n=6–8 mice/group).
