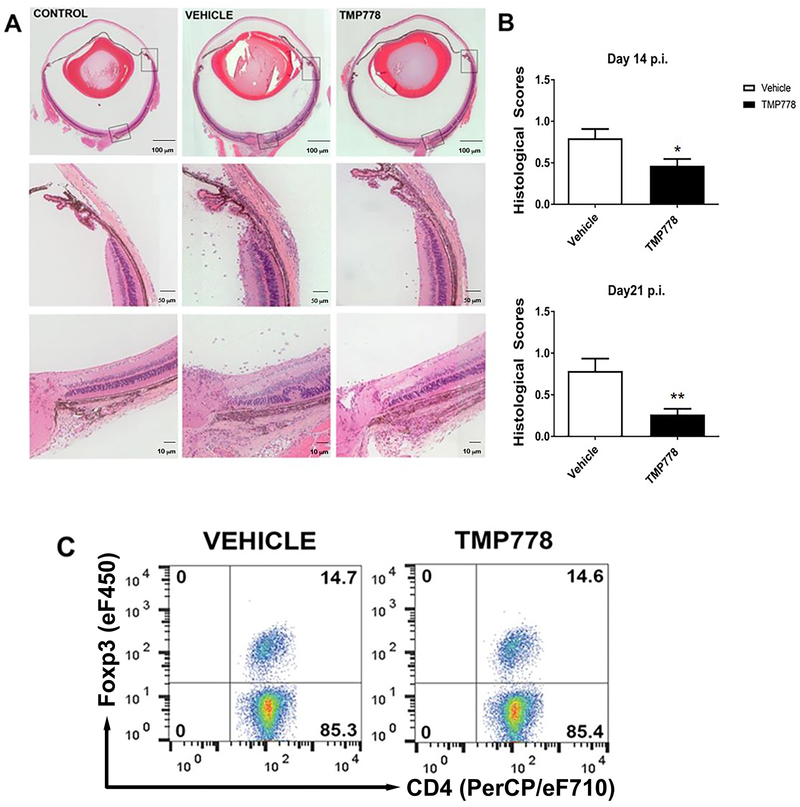
Figure 1.
Treatment with TMP778 inhibits the development of EAU in mice. Groups of B10.A mice were immunized with IRBP and their eyes were collected as detailed in the Materials and Methods . The severity of pathological changes were scored as described elsewhere [24]. (A) Eye sections of a normal control mouse and of eyes of mice treated with the vehicle or TMP778. The histopathological changes in the vehicle treated mouse eye include accumulation of inflammatory cells in the limbal and the optic nerve head areas (the entry sites for the inflammatory cells), as well as inflammatory cells migrating into the retina and a typical retinal fold. In addition, inflammatory cells are visible throughout the vitreous (histopathological score: 1.5). Changes seen in the eye of the mouse treated with TMP778 are much less severe (score: 0.5). (B) Summary of scores are shown as +- SEM (n=4-5 mice in each group) and are pooled from five independent experiments for day 14 and three independent experiments for day 21. *p <0.05; **p <0.01 Mann-Whitney U test. (C) Treg cells expressing FoxP3 do not participate in the immunosuppressive effect of TMP778. Flow cytometric analysis of pooled spleen cells from mice treated with TMP778 or the vehicle, on day 14 of treatment. The mean ratio between percentages of FoxP3+ cells in spleens of mice treated with TMP778 or the vehicle-treated control was 0.96+/−0.02. Plots are from one experiment representative of four independent experiments, with n=4-5 mice in each group.