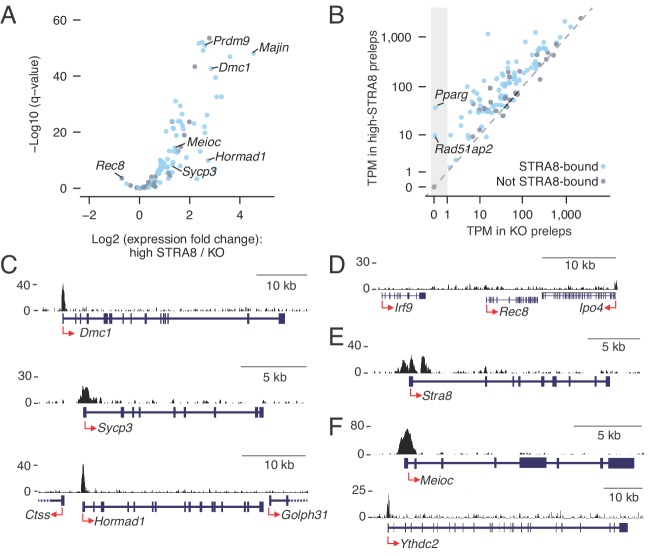
Figure 6. Coordinated upregulation of the meiotic prophase I gene expression program by STRA8.
(A) Volcano plot depicting gene expression differences between high-STRA8 and Stra8 KO preleptotene cells. Shown are 103 genes associated with meiotic prophase I in the fetal ovary (Soh et al., 2015), with 76 STRA8-bound genes shaded light blue. (B) Comparison of expression levels of meiotic prophase genes in high-STRA8 and KO preleptotene cells. The light gray region identifies genes that are not expressed in the KO. (C) Input-subtracted STRA8 ChIP-seq signal at promoters of key meiotic genes. Sequencing reads were pooled from three Stra8FLAG/FLAG ChIP replicates. Red arrows mark the TSS. (D) Lack of STRA8 ChIP-seq signal at Rec8 gene. (E) STRA8 ChIP-seq signal at its own promoter. (F) STRA8 ChIP-seq signal at promoters of Meioc and Ythdc2..