Figure 3.
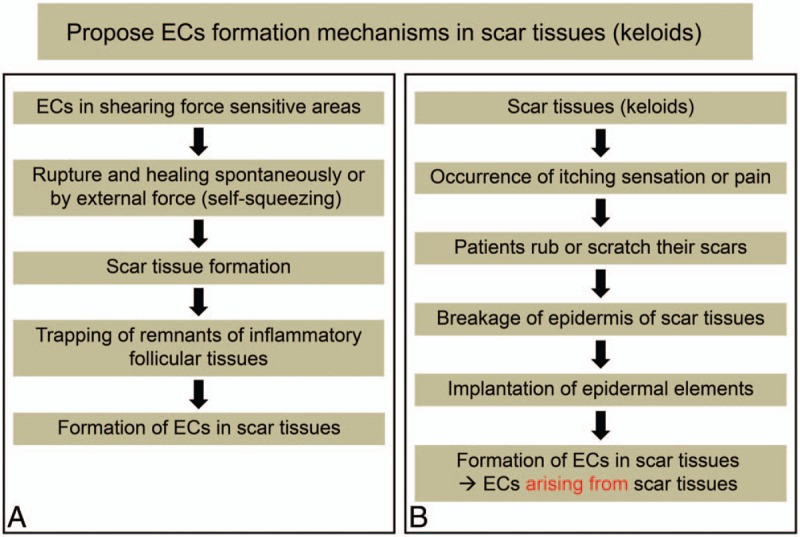
Proposed epidermal cyst (EC) formation mechanisms in scar tissues (keloid) (A) ECs in shearing force sensitive areas can result in scar tissues (keloids). Remnants of inflammatory follicular tissues can be trapped in these scar tissues, which results in the formation of ECs in scar tissues (keloid). (B) Scar tissues (keloid) can cause an itching sensation or pain. Therefore, patients rub or scratch their scars, which breaks the epidermis of the scar tissues and epidermal elements become implanted in the dermis, leading to the development of ECs within the scar tissues.
