Figure 2. rDNA copy number polymorphism express consequential and selectable metabolic phenotypes.
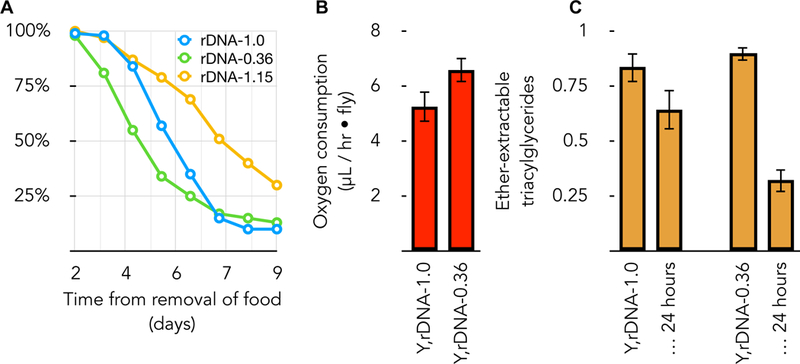
(A) Three Drosophila strains that differ only in their rDNA content exhibit different rates of starvation. Y,rDNA-1.0 is as described in Figure 1. Y,rDNA-0.36 is a derived Y chromosome with the smallest rDNA array we possess (64% of the rDNA removed). Strain Y,rDNA-1.15 is a revertant originally derived from rDNA-1.0 and contains extra rDNA copies. All strains are X, rDNA+ / Y, rDNA-(as indicated), so possess sufficient X-linked rDNA for viability and fertility. X-axis is days after removal from food, Y-axis is fraction of adults surviving at each time point. (B) Normal and smallest rDNA array-bearing flies consume oxygen at different rates. Genotypes are as described for (A). (C) Normal and smallest rDNA array-bearing flies consume ether-extractable triacylglycerides at a different rate. Populations of flies were extracted at the beginning of a starvation experiment, and again at 24 hours after removal from food. Quantification was done after thin-layer chromatographic separation (in 70:30:1 hexane:diethylether:acetic acid) and staining with 8% (w/v) H3PO4 containing 10% (w/v) copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate. Values are reported relative to purchased Triolien standards.
