Fig.2. FoxO1 inhibitor reverses DRA-induced allergic lung inflammation.
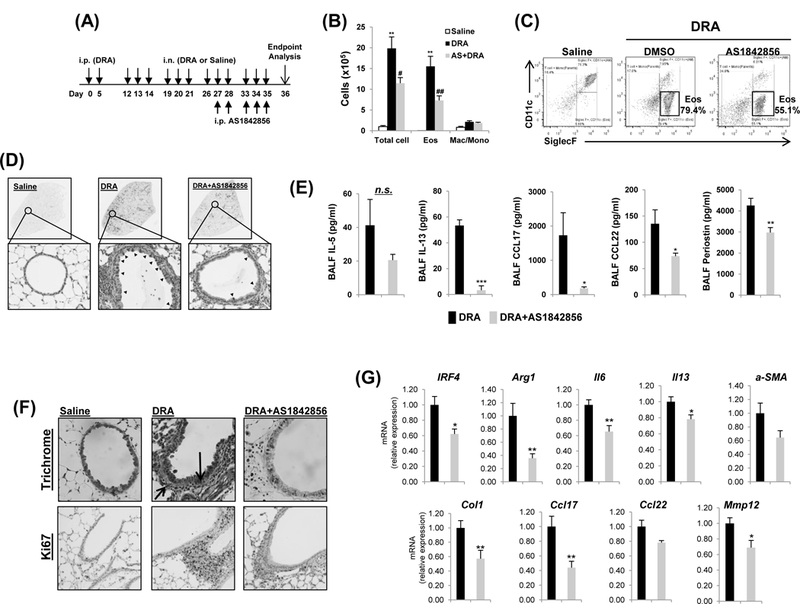
(A) Mice were sensitized and challenged by daily i.n. administration of DRA or saline, 3 days a week for 4 weeks. Prior to allergen challenge, mice were treated with vehicle or 20mg/kg of AS1842856. (B) Eosinophilic inflammation was attenuated in WT mice by pharmacologic inhibition of FoxO1. Total cells and eosinophils influx in BAL fluid were counted, analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) Cell staining for markers of eosinophils (CD45+SiglecF+CD11c-). (D) PAS stained (black arrowheads) lung sections from the mice exposed to DRA. (E) IL-5, IL-13, CCL17, and CCL22 cytokines were quantified with ELISA in BAL fluid (BALF) of AS1842856 pre-treatment group. (N=6–8). (F) Reversible effect of FoxO1 inhibitor on tissue airway remodeling in DRA-induced asthmatic lung. Sections were stained with Masson trichrome (black arrows, peribronchial) and Ki-67 (brown staining) (N=6). (G) The mRNA expression in lung tissues from DRA-induced asthma model (N=4–6). Graphs are plotted as mean ± SE. P values were obtained using a t test. *,#p<0.05, **,##p<0.01, ***p<0.001. AS, AS1842856; i.p., intraperitoneal; i.n., intranasal; Eos, eosinophil; Mac/Mono, macrophage/monocyte; n.s., not significant.
