Fig.3. FoxO1fl/flLsyMcre has attenuated DRA-induced Th2 immunity in lungs of allergic mice.
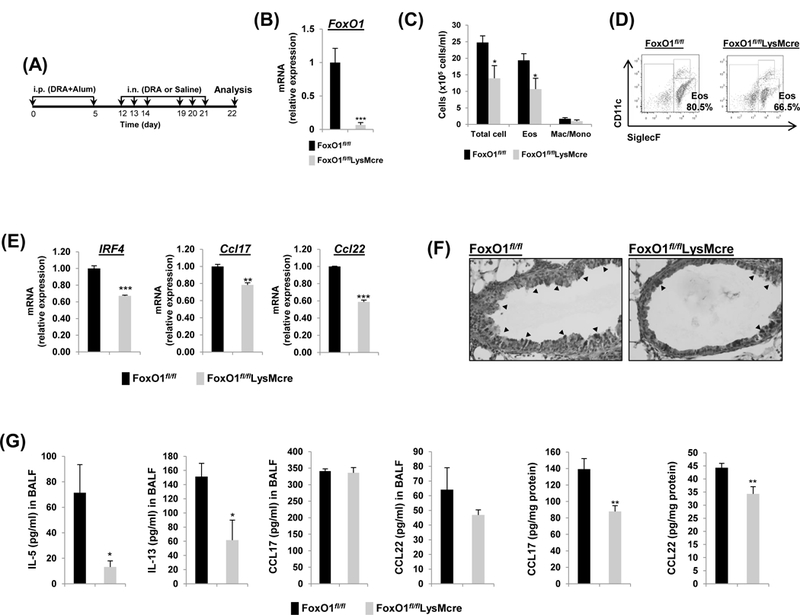
(A) FoxO1fl/fl and FoxO1fl/flLysMcre mice were sensitized and challenged by daily i.n. administration of DRA or saline, 3 days a week for 2 weeks. (B) Relative expression of FoxO1 in sorted AM. FoxO1 mRNA was analyzed by rt-qPCR. (C) Eosinophilic inflammation was attenuated in FoxO1fl/flLysMcre mice. Total cells and eosinophils influx in BAL fluid were counted, analyzed by flow cytometry. (D) Cell staining for markers of eosinophils (CD45+SiglecF+CD11c-) and AM (CD45+SiglecF+CD11c+). (E) Expression of mRNA for IRF4, Ccl17, Ccl22 in DRA-exposed murine AM from FoxO1fl/fl and FoxO1fl/flLysMcre mice. (F) PAS stained (black arrowheads) lung sections from the mice exposed to DRA. (G) IL-5, IL-13, CCL17, CCL22 were quantified with ELISA in BALF and DRA-exposed lung homogenates (N=6–8). Results are shown as mean ± SE. P values were obtained using a t test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001. i.p., intraperitoneal; i.n., intranasal; Eos, eosinophil; Mac/Mono, macrophage/monocyte.
