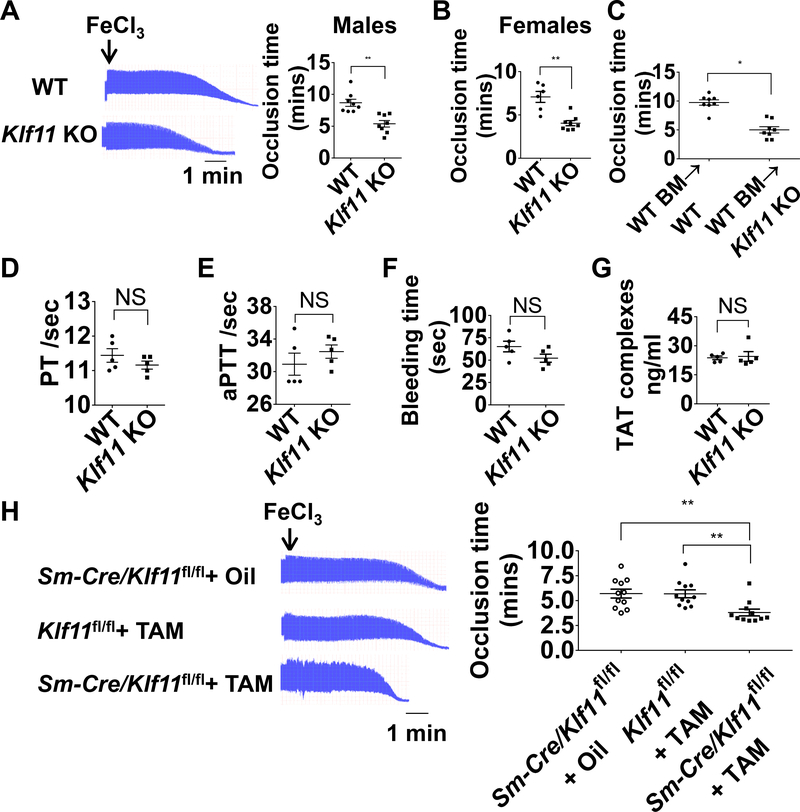
Figure 1. KLF11 (Krüppel-like Factor 11) deficiency aggravates arterial thrombosis.
A-C, The left carotid arteries of WT (wild type) and conventional Klf11 KO (knockout) mice were subjected to 10% FeCl3 to induce arterial thrombosis. A, Representative images of blood flow detected by ultrasound are shown with each division representing 8 seconds (left) and the corresponding occlusion time (right) determined in WT and Klf11 KO male mice (n=8/group). B, Occlusion time in WT and Klf11 KO female mice (n=6–8/group). C, WT male mice transplanted with WT bone marrow were designated as WT BM→WT, Klf11 KO male mice transplanted with WT bone marrow were designated as WT BM→Klf11 KO mice. The carotid artery occlusion time after bone marrow transplantation was recorded as in A (n=8/group). **P<0.01 or *P<0.05 using unpaired Student t-test. D-G, PT (prothrombin time), aPTT (activated partial thromboplastin time), bleeding time and TAT (thrombin-antithrombin) complexes were measured from WT and Klf11 KO male mice (n=5/group). NS, no significance using unpaired Student t-test (D, F, G) or nonparametric Mann-Whitney test (E). H, The left carotid arteries of Sm-Cre/Klf11fl/fl+TAM (Myh11-CreERT2/Klf11fl/fl+tamoxifen) mice and controls: Sm-Cre/Klf11fl/fl+ Oil (Myh11-CreERT2/Klf11fl/fl+ corn oi) and Klf11fl/fl+TAM (Klf11fl/fl+ tamoxifen) mice, were subjected to 10% FeCl3 to induce thrombosis. Representative images of blood flow detected by ultrasound are shown and the occlusion time in control and Sm-Klf11 KO mice was recorded (n=11/group). **P<0.01 using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test.