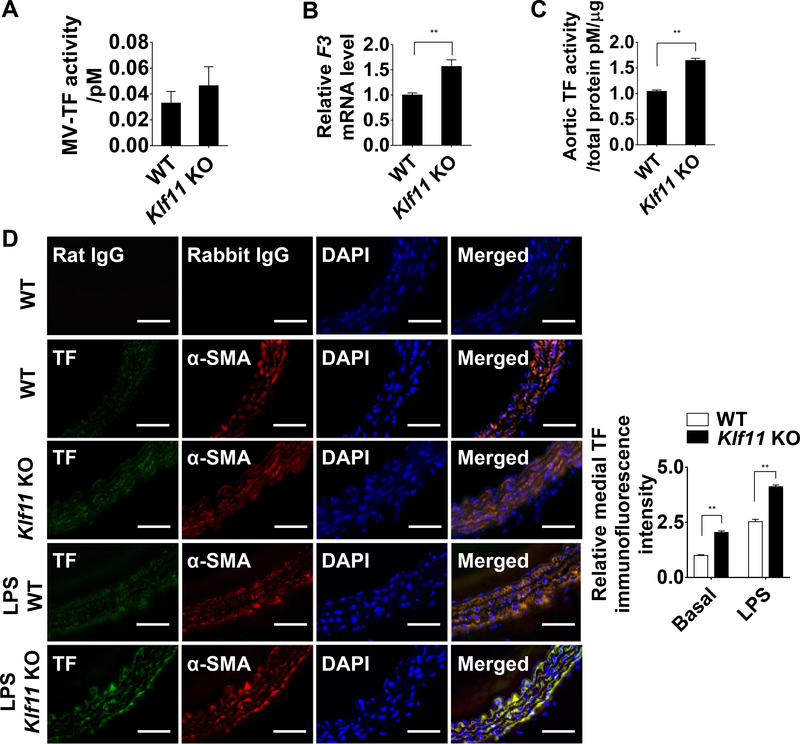
Figure 2. KLF11 (Krüppel-like Factor 11) deficiency induces TF (tissue factor) expression in arterial wall.
A, Activity of microvesicles-associated tissue factor (MV-TF) in the plasma after preincubation with IgG or TF 1H1 antibody (n=6/group). Data are presented by subtracting the amount of FXa generated in the presence of TF 1H1 antibody from the amount of total FXa generated in the presence of IgG. B, F3 mRNA level of carotid arteries from WT and Klf11 KO mice. The mRNA level was normalized by 18S and is presented relative to the WT group set as 1 (n=4/group). C, The aortic TF activity was measured and presented as in A, after preincubation with IgG or TF 1H1 antibody and normalized to the total protein quantity (n=6/group). **P<0.01 using unpaired Student t-test (A-C). D, Expression of TF (Alexa 647, displayed in green) and α-SMA (α-smooth muscle actin, Alexa 568, displayed in red) in mouse aorta at basal level or 4 hours after LPS (30 µg/kg) tail vein injection was visualized by immunofluorescence staining. Respective IgG staining was used as negative control. Scale bars=50 µm. Quantification was performed from 4 mice, randomly selecting 3 different medial regions from each specimen and dividing the TF immunofluorescence intensity by medial area (indicated by α-SMA positive cells). Data are presented relative to the basal level of WT group set as 1. **P<0.01 using two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni test.