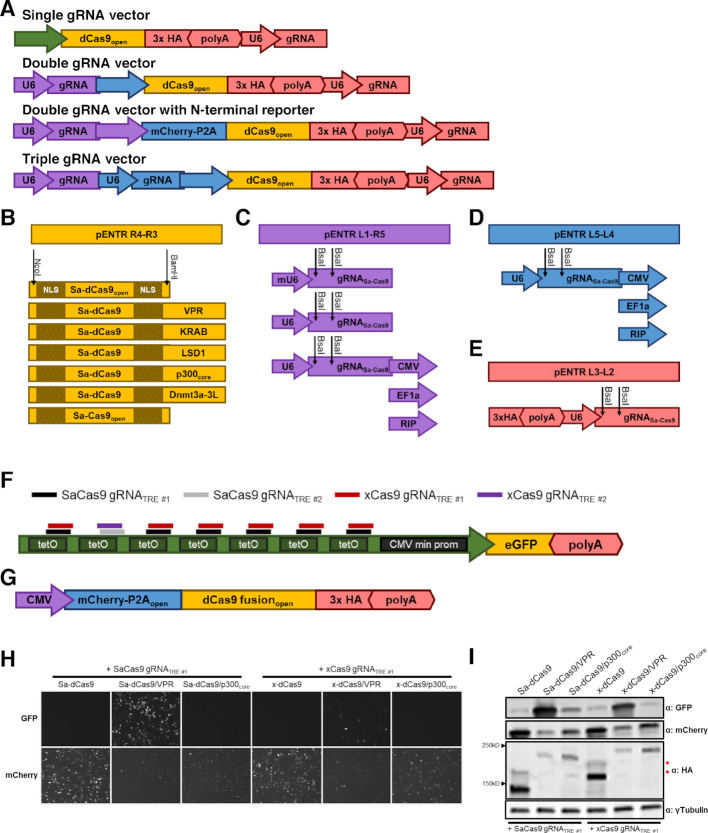
Figure 6.
The pMAGIC toolbox. (A) A schematic representation of the structure of pMAGIC-derived single, double, and triple gRNA expressing vectors. Color scheme of the components matches the respective vector combinations. (B) Sa-dCas9 and Sa-Cas9 pMAGIC fusion genes cloned into pENTR221 R4-R3 (yellow). Additional effectors can be fused to Sa-dCas9 through unique NcoI (N-terminal) and BamHI (C-terminus) restriction sites. (C) pENTR221 L1-R5 plasmids (purple) containing a Sa-Cas9 gRNA expression cassette driven by the mouse U6 (mU6) or human U6 (U6) promoter. Alternatively, a U6-driven Sa-Cas9 gRNA expression cassette can be combined with a CMV, EF1a, or RIP promoter. (D) pENTR221 L5-L4 plasmids (blue) containing a U6-driven Sa-Cas9 gRNA expression cassette and CMV, EF1a, or RIP promoter. (E) pENTR221 L3-L2 plasmid (red) containing a 3xHA epitope tag for C-terminal fusion to Sa-Cas9 proteins and a U6-driven Sa-Cas9 gRNA expression cassette. (C–E) Protospacer oligonucleotides can be ligated into BsaI digested gRNA expression cassettes. (F) Sa-Cas9 and x-Cas9 gRNA binding sites within the TRE promoter. Schematic of the TRE-driven eGFP reporter used to monitor dCas9-mediated transcriptional activation. (G) Schematic of mCherry-P2A-dCas9 expression vectors. HEK293 cells were co-transfected with plasmids for the eGFP reporter shown in panel (F), equimolar amounts of the indicated mCherry-P2A-dCas9 vectors, and the corresponding Sa-Cas9 gRNATRE#1 or x-Cas9 gRNATRE #1 plasmids. 72h after transfection, cells were (H) visualized by fluorescence microscopy and (I) cellular lysates were analyzed by immunoblot. ‘Uncleaved’ P2A products from Sa-dCas9 and x-dCas9 are designated by a red circle (•).