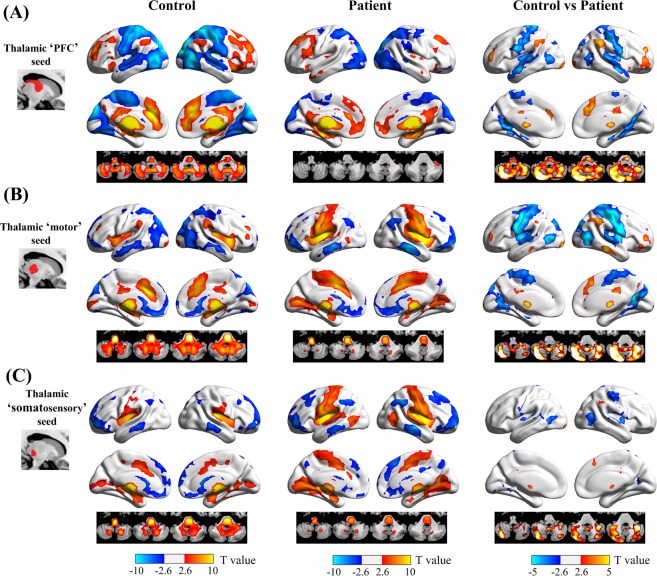
Figure 3.
Functional dysconnectivity of the PFC, motor, and somatosensory thalamus seeds in schizophrenia. For the thalamic PFC (A) and motor (B) seeds, patients with schizophrenia showed reduced functional connectivity with the dorsolateral PFC, dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, inferior parietal lobule, and cerebellum (warm colors), and increased functional connectivity with the pre- and postcentral gyri, superior and middle temporal gyri, lateral and medial occipital regions (cold colors), relative to healthy subjects. In contrast, functional connectivity of the thalamus somatosensory seed (C) was mainly restricted to the postcentral gyrus and lateral occipital region.