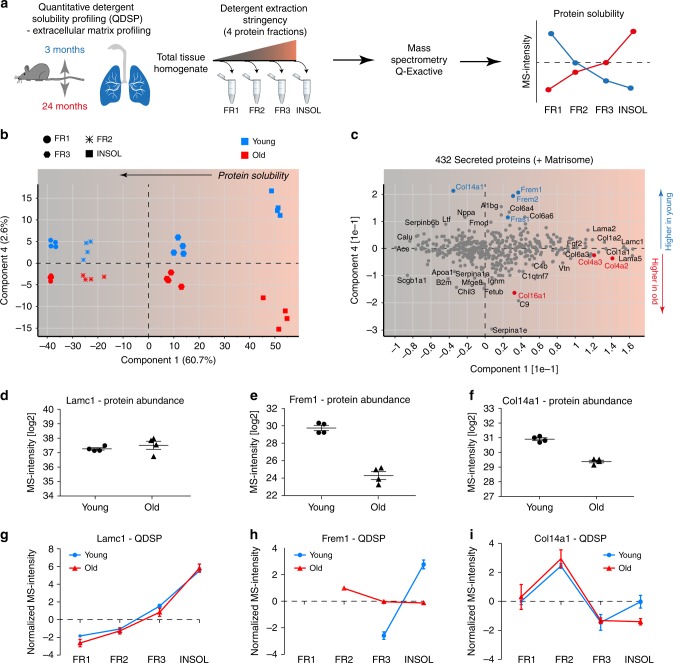
Fig. 6.
Proteome-wide detergent solubility profiling reveals changes in the extracellular matrix (ECM) architecture. a Experimental design—extraction of proteins from whole lung homogenates with increasing detergent stringency results in four distinct protein fractions, which are analyzed by mass spectrometry (MS). b The projections of a principal component analysis (PCA) of 432 proteins with the annotation ‘secreted' in the Uniprot and/or Matrisome database separate the four protein fractions, indicated by symbol shape, in component 1 and the age groups, as indicated by color, in component 4. c The loadings of the PCA are shown. d–f Relative differences in MS intensity (abundance) of the indicated proteins. g–i The normalized MS intensity across the four protein fractions from differential detergent extraction highlights changes in protein solubility between young and old mice for the indicated proteins. Error bars represent the standard error of the means (n = 4)