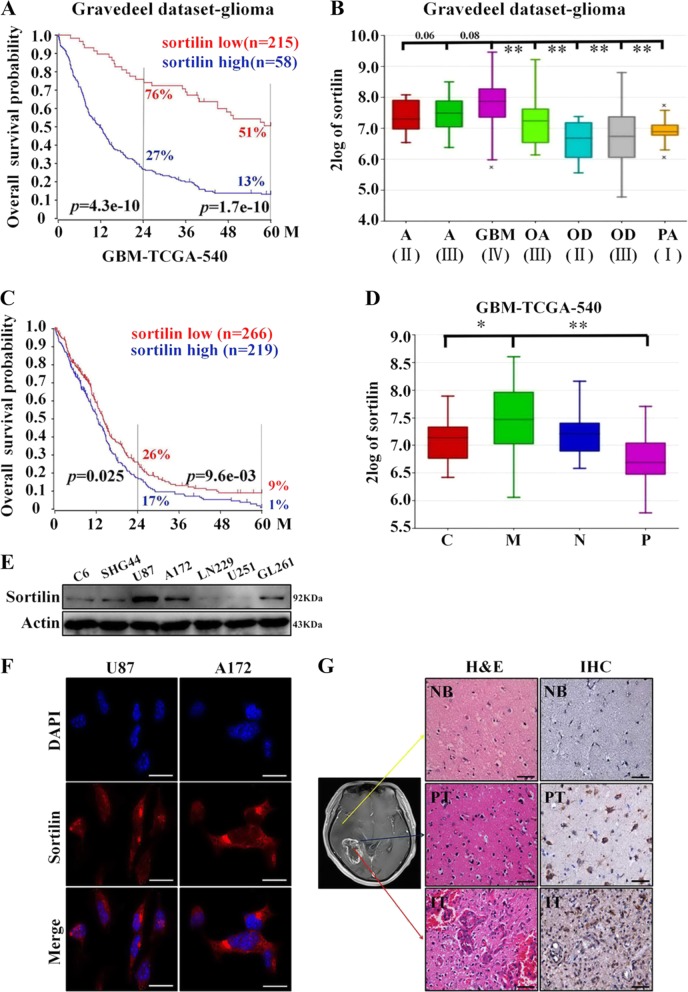
Fig. 1. The expression of sortilin is elevated in highly invasive glioblastoma subtypes and negatively correlated with patient prognosis.
a Kaplan–Meier analysis of the 2-year survival rates and the 5-year survival rates of patients with low level and high level of sortilin from the RGAVP, which includes 273 different grades of glioma cases, p-value was determined using the log-rank test. b The expression levels of sortilin in different pathological grades of glioma from the RGAVP (A astrocytoma, GBM glioblastoma multiforme, OA oligoastrocytoma, OD oligodendroglioma, PA pilocytic astrocytoma; II, III, IV WHO grade classification of glioma), p-value was determined using the independent samples T-test (**p < 0.01). c Kaplan–Meier analysis of the 2-year survival rates and the 5-year survival rates of patients with low level and high level of sortilin from the Tumor GBM-TCGA-540 dataset (n = 485); p-value was determined using the log-rank test. d The expression levels of sortilin in different subtypes of glioblastoma (C classical subtypes, M mesenchymal subtype, N neural subtype, P proneural subtype) were analyzed on the R2 microarray analysis and visualization platform, p-value was determined using the independent samples T-test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). e Western blotting analysis of sortilin protein expression in glioblastoma cell lines (C6, SHG44, U87, A172, LN229, U251, GL261). f Representative immunofluorescence images of sortilin (red) and nucleus (blue) in U87 and A172 cell lines, scale bar = 50 μm. g Representative H&E (scale bar = 100 μm), IHC (sortilin, scale bar = 100 μm), and IHC (sortilin combined with Ki67, scale bar = 20 μm) stained slices from the different regions of human glioblastoma specimens (NB normal brain, PT peritumor, IT intratumor).*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01