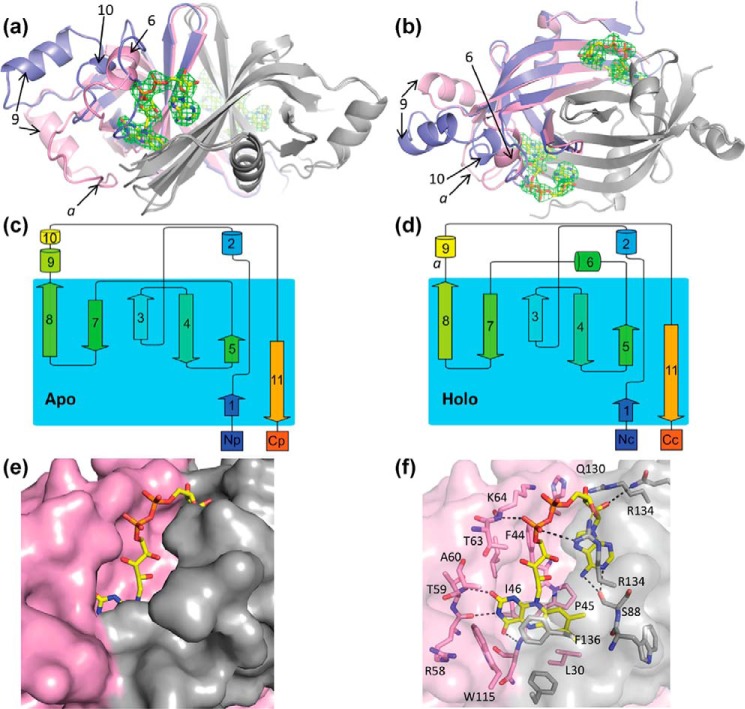
Figure 4.
Structure of apo- and holo-FAD Fsq. a and b, side (a) and top (b) views of the overlaid structures of apo (blue, chain P) and holo (pink, chain B) Fsq. The secondary chain of the dimer for both structures is shown in gray. FAD bound to the holo-structure is shown in yellow and the electron density for the cofactor on both binding sites of the dimer is shown, representing the Fo − Fc omit map contoured at 3 σ. Key loops and α-helixes are labeled to reference parts c and d. c and d, topology maps of the apo- and holo-structures, respectively, adapted from the cartoons generated by Pro-origami. e, solvent-accessible surface of Fsq showing the buried flavin moiety in the holo-structure. f, residues involved in FAD binding.