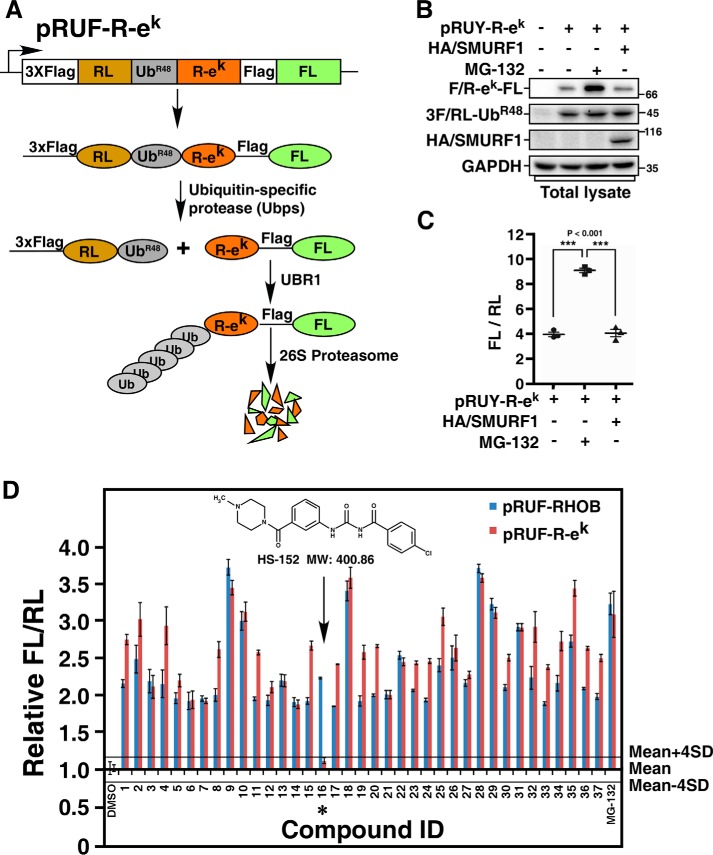
Figure 3.
Counterscreen using the N-end rule pathway. A, a schematic of the pRUF–R-ek construct. The pRUF–R-ek is designed similarly to pRUF-RHOB (Fig. 1A) except that triple FLAG-tagged FL-RHOB is replaced by R-ek–FLAG-FL. B, immunoblotting assay of the steady-state levels of R-ek–FL. HEK293T cells were transfected with pRUF–R-ek with or without HA/SMURF1 as indicated. After 3 h treatment with or without 10 μm MG-132, steady-state protein levels were determined by immunoblotting total cell lysates using indicated antibody. C, luciferase assay of R-ek–FL. HEK293T cells were transfected with or without HA/SMURF1 and pRUF–R-ek, and treated with or without MG-132 as in (B). The activities of FL and RL were then measured and plotted as FL/RL. D, counterscreen of selected compounds from the primary screen. HEK293T cells transfected with pRUF–R-ek were treated 6 h with 10 μm of each of the 37 compounds identified in the primary screen. DMSO and MG-132 were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. The effect of each compound on the FL-RHOB/RL or R-ek–FL/RL ratio was plotted relative to the mean of the eight DMSO-treated control wells, respectively. Solid lines represent the mean ± 4 × S.D. of the DMSO controls, as indicated. Arrow and asterisk show the compound that had minimal effect on R-ek–FL/RL ratio.