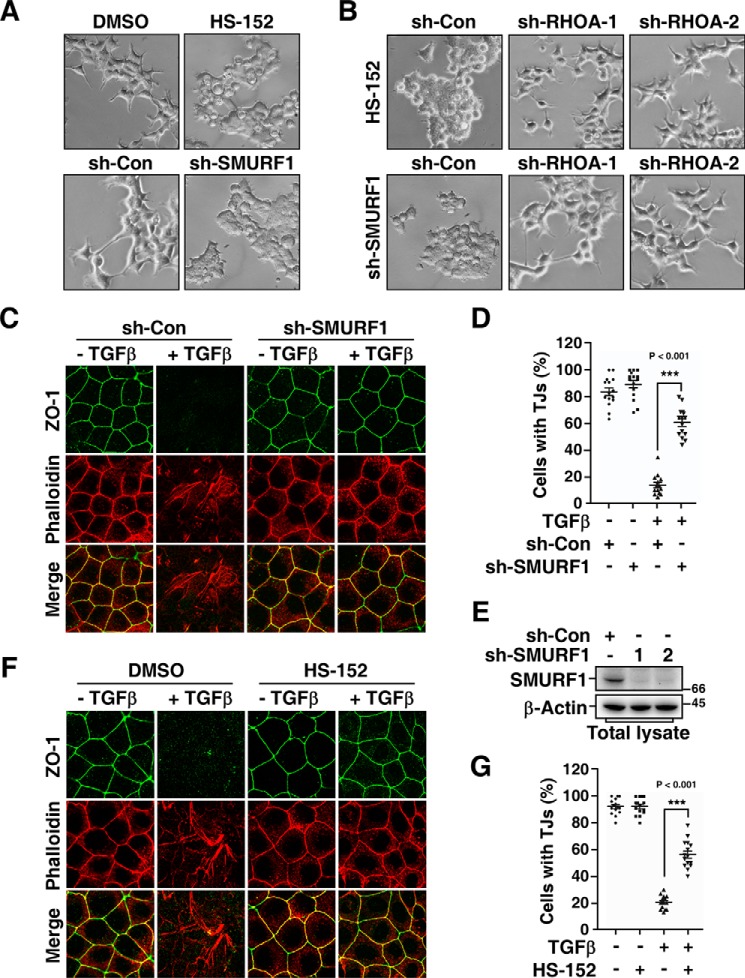
Figure 6.
HS-152 inhibits cell protrusive activity and TGFβ-induced EMT. A, HS-152 has a similar effect with SMURF1 shRNA on inhibiting protrusive activity of HEK293T cells. Twenty-four h after being transfected with control shRNA (sh-Con) or shRNA against SMURF1 (sh-SMURF1) (lower panel), or overnight after being treated with or without 1 μm HS-152 (upper panel) as indicated, HEK293T cell morphology was imaged by phase contrast microscopy. B, HS-152–caused loss of protrusion depends on RHOA. HEK293T cell morphology was imaged by phase contrast microscopy 24 h after co-transfection with the indicated combination of sh-SMURF1 and sh-Con or shRNA against RHOA (sh-RHOA) (lower panel), or treated another 4 h with DMSO or 1 μm HS-152 20 h after transfection with sh-Con or sh-RHOA (upper panel) as indicated. C and D, knockdown of SMURF1 blocks TGFβ-induced EMT. MDCK cells transduced with lentivirus encoding sh-Con or sh-SMURF1 were treated 20 h with or without 100 pm TGFβ, and then subjected to immunofluorescence assay. ZO-1 staining was detected with an anti-ZO-1 antibody (green), and F-actin was visualized with Texas red-conjugated phalloidin (red) (C). The percentages of cells with tight junctions (TJs) were plotted in (D). Five random areas were counted for each experiment and data of three independent experiments were assessed and represented as mean ± S.D. (D). E, knockdown efficiency of SMURF1. MDCK cells transduced with lentivirus encoding sh-Con or sh-SMURF1 were subjected to immunoblotting assay to examine the knockdown efficiency of SMURF1. F and G, HS-152 inhibits TGFβ-induced EMT. MDCK cells pretreated 12 h with DMSO or 0.05 μm HS-152 were treated another 20 h with or without 100 pm TGFβ and then subjected to immunofluorescence assay (F). Quantification of cells with tight junctions was as in (D).