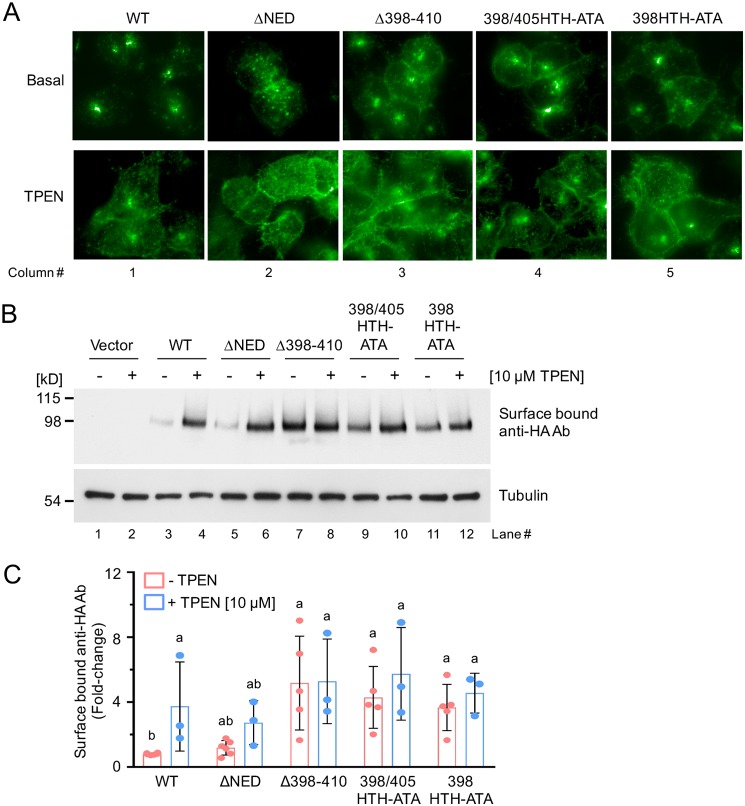
Figure 3.
Zinc-dependent relocalization of the mZIP4 mutant proteins. A, immunofluorescence microscopy analysis of HEK293 cells expressing each of the mZIP4-HA mutant proteins, which are exposed to either basal medium (∼2 μm zinc) or medium containing 10 μm of the zinc chelator TPEN for 1 h. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and blocked prior to detection of WT and mutant mZIP4-HA proteins using anti-HA antibodies followed by anti-mouse Alexa 488 secondary antibodies. B, analysis of plasma membrane levels of WT and mutant mZIP4 proteins following TPEN treatment. Immunoblots were used to detect anti-HA antibodies bound to the surface of HEK293 cells expressing WT or mutant mZIP4 proteins after exposure to either basal medium (−) or medium containing 10 μm TPEN (+) for 1 h. Levels of anti-HA antibodies bound to mZIP4-HA at the plasma membrane were determined using Western blots as described under “Experimental procedures.” Tubulin protein was detected in each sample to indicate equal protein loading. C, quantification of surface bound anti-HA antibodies in HEK293 cells expressing mZIP4 WT and mutant proteins (Fig. 3B). Relative fold-changes compared with basal condition of WT mZIP4-HA are presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 3–6). Values with one different letter are significantly different from each other (p < 0.05). Statistics: two-way ANOVA, Sidak's post hoc test.