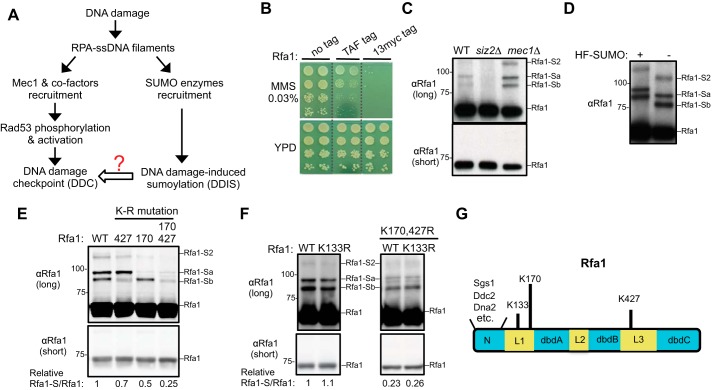
Figure 1.
Examining the sumoylation of untagged Rfa1 and previously identified Rfa1 sumoylation sites. A, simplified schematic of the DNA damage response involving the Mec1 checkpoint and the DNA damage–induced sumoylation, with a focus on the events that require RPA-coated ssDNA. B, addition of a TAF or Myc tag on the C-terminal of Rfa1 sensitizes the cells toward DNA damaging agents. 10-fold serial dilution of cells of the indicated genotypes were spotted and growth was assessed after incubation at 30 °C for 3 days. The dashed lines indicate removal of superfluous rows. C, detection of the sumoylation of untagged Rfa1 in MMS conditions. Cells were treated with 0.02% MMS, and protein extracts from the indicated strains were examined by immunoblotting using anti-Rfa1–specific antibody (15). Rfa1-Sa and -Sb denote mono-sumoylated Rfa1 species, and Rfa1-S2 denotes di-sumoylated Rfa1 species. Molecular weight is indicated at the left of the blots. D, Rfa1 sumoylation bands exhibit expected up-shifts when a larger variant of SUMO containing His6-FLAG tag (HF-SUMO) is present. To better detect band shift, WT cells were treated with 0.3% MMS to increase Rfa1 sumoylation levels. E, mutation of lysines 170 and 427 to arginine reduces Rfa1 sumoylation. Specifically, rfa1Δ cells were supplemented with CEN-based plasmids expressing either WT or mutant Rfa1 driven by Rfa1 endogenous promoter. Cells of the indicated genotypes were treated and examined as in panel D. rfa1-K170R and rfa1-K427R reduced the signals of the Rfa1-Sa and -Sb sumoylation bands, respectively. The relative ratios of the sumoylated Rfa1 signals to those of unmodified Rfa1 are indicated below. F, mutation of lysine 133 to arginine does not reduce Rfa1 sumoylation in WT background (left) or in rfa1-K170, 427R background (right). Experiments were done and labels are indicated as in panel E. G, schematic of the budding yeast Rfa1 protein domains. Some known interactors for the Rfa1 N-terminal domain are indicated. The three lysine residues previously reported as Rfa1 sumoylation sites and representative proteins that bind to the Rfa1 N-terminal domain are also indicated.