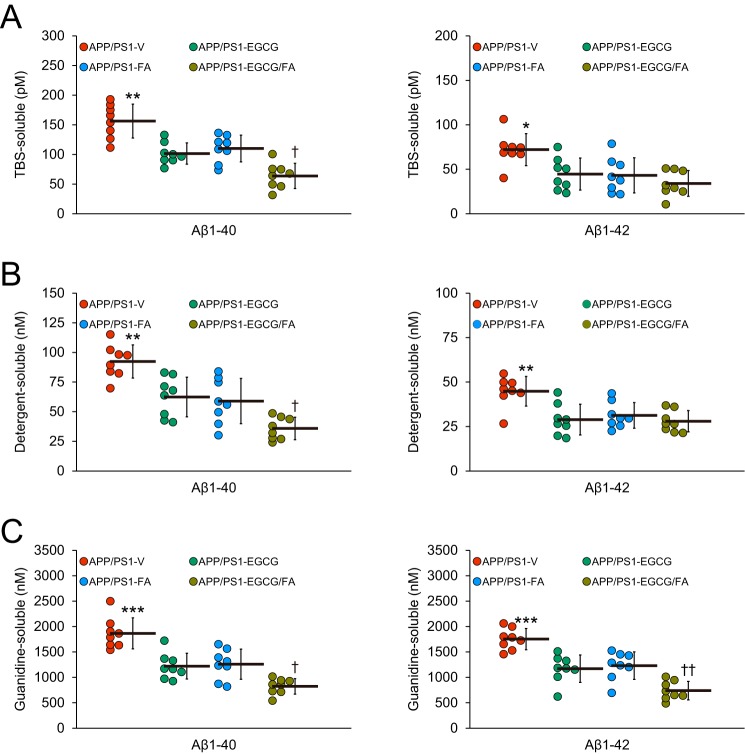
Figure 4.
Combination therapy with EGCG and FA significantly lowers Aβ levels. A, TBS-soluble; B, detergent-soluble; and C, 5 m guanidine HCl-extractable fractions from brain homogenates were individually measured by sandwich ELISA for human Aβ(1–40) (left) and Aβ(1–42) (right). Data were obtained from APP/PS1 mice that received vehicle (APP/PS1-V, n = 8), EGCG (APP/PS1-EGCG, n = 8), FA (APP/PS1-FA, n = 8), or EGCG plus FA (APP/PS1-EGCG/FA, n = 8) for 3 months beginning at 12 months of age (mouse age at sacrifice = 15 months) for A–C. Data for A–C are presented as standard deviations of the means. Statistical comparisons for A–C are between-groups for each Aβ species. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p ≤ 0.001 for APP/PS1-V versus the other treated mice; †, p < 0.05; ††, p < 0.01 for APP/PS1-EGCG/FA versus APP/PS1-EGCG or APP/PS1-FA mice. V, vehicle.