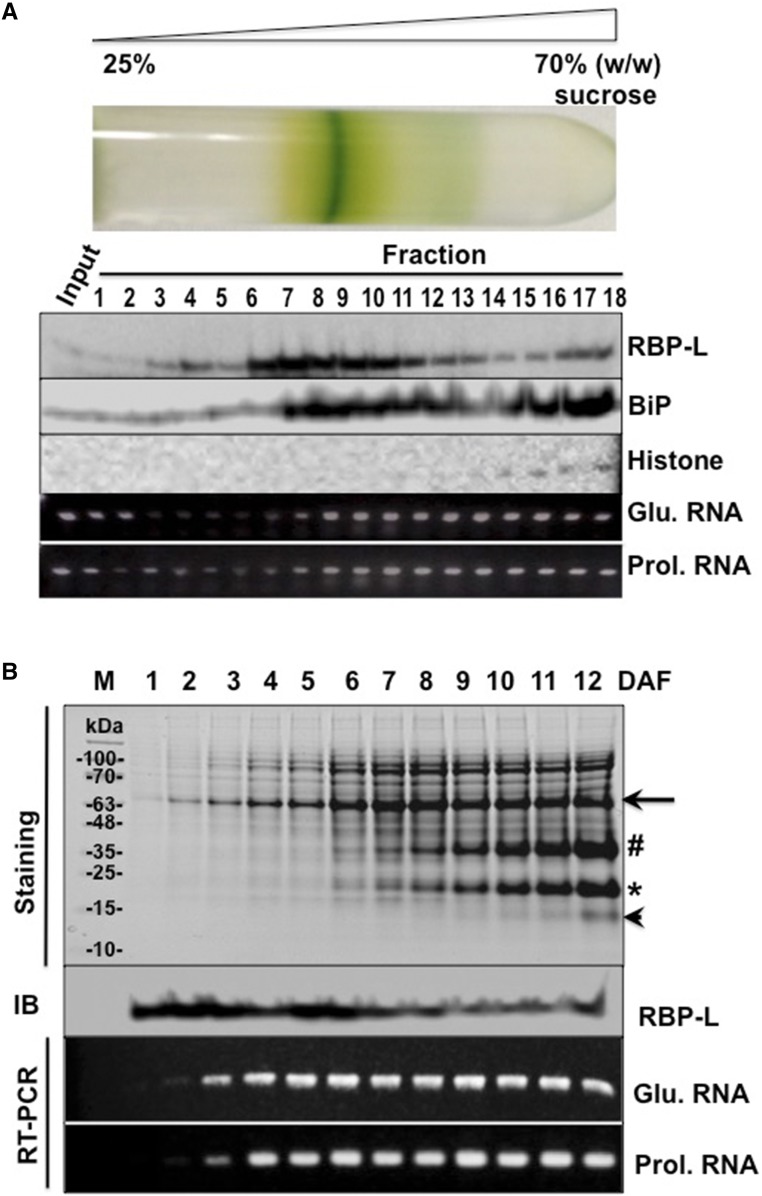
Figure 4.
The association of RBP-L with glutelin and prolamine mRNAs in developing rice grains. A, The distribution of RBP-L, glutelin, and prolamine mRNAs, histone, and BiP as resolved by Suc density gradient centrifugation. Samples from the Suc gradient were collected from the top (25% [w/w] Suc) to bottom (70% [w/w] Suc) and subjected to SDS-PAGE, immunoblot analyses, and RT-PCR. Input, rice seed lysate sample before centrifugation. Histone H3 and BiP were used as nuclear and the ER markers, respectively. Glutelin and prolamine mRNA distribution was assessed by RT-PCR using the total RNA isolated from each fraction. B, Expression of RBP-L protein and glutelin/prolamine RNAs during rice seed development. Total proteins and RNAs extracted from developing rice seeds, collected daily from 1 to 12 DAF, were subject to SDS-PAGE (Coomassie brilliant-blue–stained gel) followed by immunoblot analysis or by RT-PCR using glutelin- and prolamine-specific primers (RT-PCR), respectively. Black arrow, Glutelin precursor; #, acidic subunit; *, basic subunit; arrowhead, prolamine polypeptide; Glu. mRNA, Glutelin RNA; Prol. mRNA, prolamine RNA; IB, immunoblot analysis.